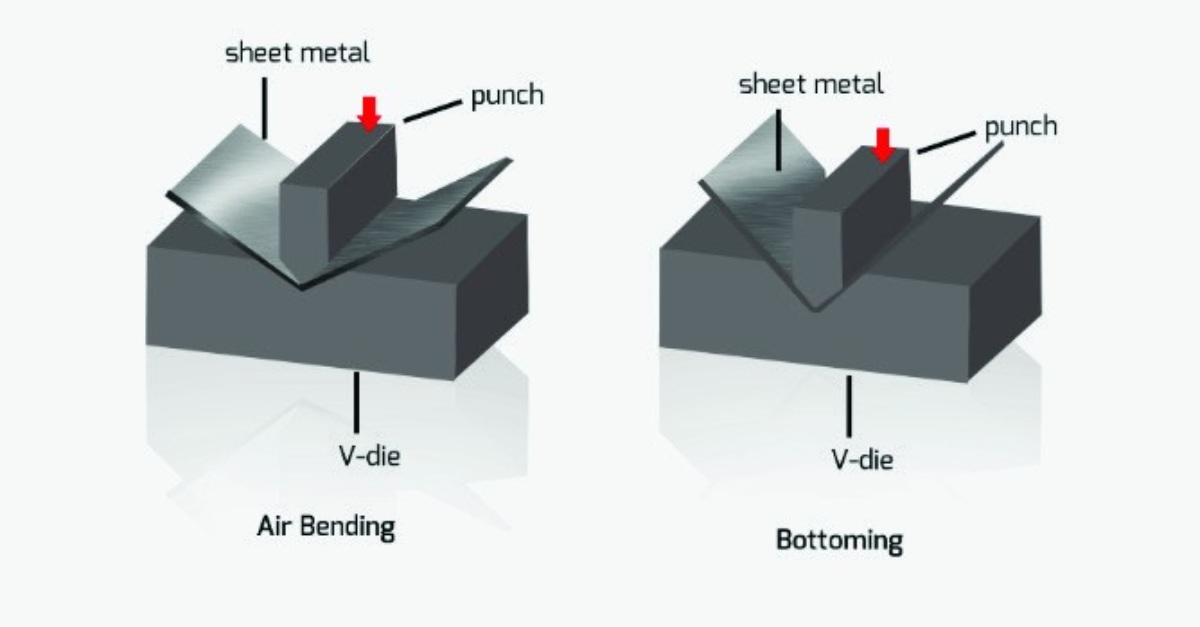
Air bending and bottom bending are two important ways to bend metal on a cnc press brake. Air bending bends metal by pushing the sheet partway into a die. Bottom bending shapes metal by pressing it all the way into the die. In sheet metal work, picking the right way affects how good and fast the work is.
| Bending Method | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Air Bending | Quicker, can change easily | Makes many parts, needs less accuracy |
| Bottom Bending | More exact, less bending back | Needs tight fit, keeps parts the same |
KRRASS is a leader with new press brake ideas. Their cnc machines help people get great results. Readers will find helpful tips for picking the best way to bend.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Air bending is quick and easy to change. You can make different angles fast. You do not need new tools for each angle.
- Bottom bending is very accurate. It is good for jobs that need exact shapes. It is also good when you need to make the same part many times.
- KRRASS machines help both bending types. They use smart controls to work better. This makes the work faster and more correct.
- Operators should pick air bending for custom parts. It is also best for small batches. Bottom bending is better for making many parts. It is good for jobs that need to be very exact.
- It is important to take care of CNC press brakes. Clean them every day. Check them every week. This helps them last longer and work well.
- Operators must know about springback. They can change how they bend to fix this problem.
- Operators need training to use CNC press brakes safely. Training helps stop mistakes and accidents.
- Quality checks are important. Calibrating and looking at parts helps keep the work good.
Air Bending Process
Overview
Air bending is a popular way to shape sheet metal. It uses a punch and die, but the punch does not go all the way down. There is a gap between the punch and the die. This gap is why it is called air bending. Operators can change the angle by moving the punch up or down. KRRASS Sheet Metal Bending Machines have smart controls. These controls help make air bending fast and accurate.
The main steps in air bending are:
- Die Preparation: Operators pick the right die for the metal and angle.
- Placing the Metal Sheet: They put the sheet on the die and line it up with the punch.
- Apply the Pressure: The punch goes down and bends the metal, but does not touch the bottom of the die.
- Forming the Bend: The metal bends into an arc. The angle depends on how deep the punch goes and the shape of the die.
- Releasing the Material: When the angle is reached, the punch goes up. The operator takes out the part.
- Evaluate and Adjust: Operators look at the bend and make changes if needed.
This way of bending lets operators change things quickly. It works for many kinds of jobs.
Characteristics
Air bending has special features that make it different from other ways to bend metal. The table below shows its main features:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Operators can make many angles with the same tools. |
| Efficiency | It needs less force, so it is faster and easier on the machine. |
| Versatility | Works with many types of metal and thicknesses. |
| Influence of Die Width | The die width changes the bend radius, giving more control. |
| Springback | The metal may bend back a little, so operators must fix it. |
KRRASS machines help with these features. They have controls that make it easy to adjust.
Advantages
Air bending has many good points for making sheet metal parts:
- It needs less force than other ways, so the press brake lasts longer.
- Operators can use one die for many angles, which saves time and money.
- It is easy to change setups, so it is good for small jobs or custom work.
- Air bending works with many metals and thicknesses.
- KRRASS machines use smart technology to make springback smaller and improve accuracy.
Many people pick air bending because it is fast, flexible, and saves money. This way helps make parts quickly and with good quality, especially with new machines.
Disadvantages
Air bending has many good points, but it also has some problems. Operators and manufacturers need to think about these issues. The table below shows the most common problems with this method:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High initial cost | Operators must buy advanced machines and keep them working. Special training costs extra money. |
| Material size and thickness limitations | Air bending works best with certain sizes and thicknesses. Very thick or big sheets may not bend well. |
| Require high pressure | The process uses a lot of pressure. Thin materials can get damaged if not handled right. |
| Restricted to simple geometries | Air bending makes simple bends. Complex shapes need other methods. |
| Need professional training | Operators need special training to use the machines safely and well. |
| Space requirement | These machines are large and take up a lot of space. This can change how a workshop is set up. |
Note: Operators should check their workspace and skills before picking air bending for a job.
Springback is another problem in air bending. When the punch goes up, the metal can bend back a little. This can change the final angle. Operators often need to change the punch depth or use smart controls, like those on KRRASS Sheet Metal Bending Machines, to fix this. Die width also changes the bend radius. Picking the right tool is important to get the right shape.
Applications
Air bending is used in many industries and projects. It is flexible and fast, so many people like to use it for sheet metal work. Here are some common uses:
- Prototyping and Custom Parts: Manufacturers use air bending to make prototypes or custom parts. They can change angles quickly, which helps them work faster.
- Short Production Runs: Air bending is good for small batches. Operators can switch jobs fast without changing tools, which saves time.
- General Fabrication: Many workshops use air bending for daily work. It works with many metals and thicknesses, so it fits many jobs.
- Automotive and Aerospace: These industries use air bending for parts that do not need very tight accuracy. The process is quick and helps make parts fast.
- Electrical Enclosures and Cabinets: Air bending is used to make panels and boxes where medium accuracy is okay.
KRRASS Sheet Metal Bending Machines help with these jobs by giving advanced controls and automation. Operators can get the same results every time, even with different materials or busy schedules. Air bending is versatile, so manufacturers can react fast to new customer needs and market changes.
Bottom Bending Process
Overview
Bottom bending is an old way to bend metal on a press brake. Operators put the metal plate between the upper and lower molds. The upper mold moves down and pushes the metal into the die. This makes the metal take the shape of the die. Bottom bending gives a lot of control over the bend angle. It is good for jobs that need to be very exact. Many manufacturers use bottom bending when they need accuracy and the same results every time. KRRASS has special tools and machines for bottom bending. These help make sure every bend is the same.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The plate goes between the upper and lower molds. |
| 2 | The upper mold moves down and presses on the plate. |
| 3 | The plate bends to the angle needed. |
| 4 | The bent plate comes out of the press brake. |
Bottom bending has been important since the first press brakes. Air bending is now more common, but bottom bending is still needed for very exact work.
Characteristics
Bottom bending is not the same as air bending. It needs more force and stronger tools. Each bend matches the die angle, so you need a new die for each angle. This way gives better accuracy and less springback than air bending. The metal keeps its shape after bending, so you do not need to fix it much. But bottom bending can scratch or mark the metal more because it presses hard against the die.
| Characteristic | Bottom Bending | Air Bending |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | More accurate, good for tight jobs | Good for jobs that do not need to be exact |
| Flexibility | Not as flexible, needs new dies | More flexible, same tools for many angles |
| Surface Finish | Can scratch the metal | Softer on the metal, better finish |
| Force Requirements | Needs more force and stronger tools | Needs less force, easier on tools |
| Cost | Costs more because of many dies | Cheaper, fewer dies needed |
KRRASS makes bottom bending better with special tools and smart controls. Their machines check the angle as you bend. This helps operators get the right bend every time.
Advantages
Bottom bending has some big benefits for press brake work. It is very accurate because each bend matches the die. This makes it great for making lots of parts that must be the same. There is less springback, so the metal stays in shape after bending. Operators do not need to fix the parts as much, which saves time.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Accuracy | Each bend matches the die, so parts are the same. |
| Less Springback | The metal keeps its shape, so less fixing is needed. |
| Great Repeatability | Good for making many parts that must all be alike. |
KRRASS bottom bending uses very exact tools and smart machines. Their press brakes have controls that help keep every bend the same. These features help factories make parts that meet high standards. Bottom bending is still a good choice for jobs that need perfect bends and steady results.
Disadvantages
Bottom bending is very accurate, but it has some problems. These problems can make work harder and cost more money in a shop.
- Shops need special dies for each bend angle. If a job needs angles that are not 90 degrees, they must buy more tools. This makes the starting cost of press brake forming higher.
- Tooling costs can go up fast if designs change a lot. Every new angle or part shape might need a new die. This adds more spending to the project.
- The metal touches the die directly and can get scratched or marked. This is bad for parts where looks are important or the surface will show.
- Skilled operators are needed for bottom bending. They must know how to set up press brake forming the right way. If they make mistakes, the machine or tools can get damaged.
- Shops have to plan for longer setup times. Changing dies for new angles or parts takes time and slows down the work.
Note: KRRASS has smart machines that help with these problems. Their machines make press brake forming more exact and help workers get the same results with fewer mistakes.
Applications
Bottom bending is used in many jobs where parts must be the same every time. Factories pick this way when they need tight sizes and good part quality.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Car factories use bottom bending for parts that must fit just right. This way makes sure every piece meets tough rules.
- Aerospace Components: Airplane parts need exact angles and shapes. Bottom bending gives the accuracy needed for safety and good work.
- Electrical Enclosures: Makers of control panels and boxes use bottom bending. It helps them make parts that fit together with no gaps.
- Appliance Production: Companies use press brake forming to make covers and panels for appliances. This keeps every part the same size and shape.
- Mass Production: When a shop must make thousands of the same part, bottom bending gives the repeatability needed for big jobs.
KRRASS machines help with these jobs by giving smart controls and tool choices. Their technology lets workers do press brake bending with confidence. Each part will meet the needed rules. Bottom bending is still a top pick for jobs where quality and sameness are most important.
Air Bending vs. Bottom Bending
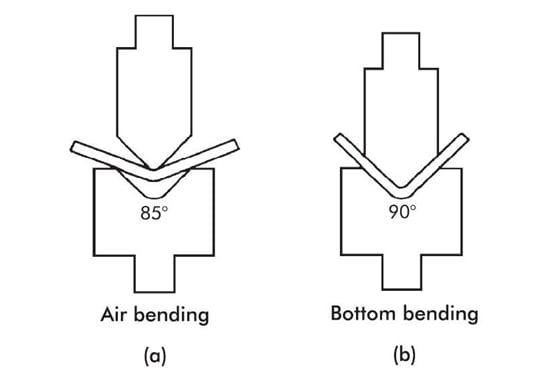
Accuracy
Accuracy is very important in press brake forming. People often look at air bending and bottom bending to see which is better for their job. Bottom bending is more accurate. The punch pushes the metal all the way into the die. This helps stop springback and keeps the angle close to the die shape. Air bending leaves a space between the punch and die. This space can cause more springback and small mistakes in the bend angle.
The table below shows how each method is different for accuracy:
| Method | Bending Angle Error | Springback Impact | Bending Force Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Bending | ~0.5 degrees | Higher due to material strength | Relatively low |
| Bottom Bending | Lower | Less after load release | Higher |
Bottom bending is best for jobs that need very exact sizes and shapes. Air bending works well when small changes in the angle are okay. KRRASS machines help workers get good accuracy with both ways. They use smart controls and feedback to help.
Flexibility
Flexibility means how easy it is to change angles, materials, or thicknesses. Air bending is very flexible. Workers can use the same tools for many angles. They just change how far the punch goes down. Air bending works with many types of metal and thicknesses. It helps stop cracking and lets workers switch jobs fast.
Bottom bending is less flexible. Each angle needs its own die. Workers must change tools for every new angle or part. This takes more time and makes it harder to do new jobs quickly.
The table below shows how flexible each way is:
| Bending Method | Flexibility | Force Requirement | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Bending | High | Requires less force | Suitable for a range of materials, reduces cracking |
| Bottom Bending | Less | Requires more force | Best for materials that can handle higher stresses |
Shops that do lots of custom work or small batches like air bending. Bottom bending is better for making lots of the same part.
Tooling
Tooling changes how much press brake forming costs and how fast it goes. Air bending uses fewer tools. One die can make many angles. Workers only change how deep the punch goes and the shape of the tool. This saves time and money, especially for shops with many jobs.
Bottom bending needs a special die for each angle. This means more tools and more setup time. But it also gives better accuracy and repeatable results. The punch and die must fit together tightly. The metal must be the same each time for the best results.
- Air bending needs careful control of punch depth and tool shape. This lets workers change angles easily but may not be the most accurate.
- Bottom bending uses tight-fitting tools and full contact between punch and die. This gives the same results every time but costs more for tools.
- Quick-change tools and segmented tools help both ways. These tools make setup faster and let workers make custom setups. This helps save time and reduce waste.
KRRASS has smart tooling for both air bending and bottom bending. Their machines let workers change tools quickly and use segmented setups. This helps shops work faster and make better parts.
Material
The kind of metal you pick is very important. Each metal bends in its own way. Operators need to know how springback and shape change with each method.
| Material Type | Springback (Degrees) | Bending Method |
|---|---|---|
| 304 stainless steel | 2 to 3 | Air Bending |
| Mild aluminum | 1.5 to 2 | Air Bending |
| Cold-rolled steel | 0.75 to 1.0 | Bottom Bending |
| Hot-rolled steel | 0.5 to 1.0 | Bottom Bending |
| Copper and brass | 0.00 to 0.5 | Bottom Bending |
Stronger metals like stainless steel bend back more with air bending. Softer metals, such as copper and brass, keep their shape better with bottom bending. Operators pick bottom bending for metals that need sharp angles and less springback.
- Air bending means the tool does not touch the metal as much. The final angle depends a lot on the metal’s own traits.
- Bottom bending pushes the metal all the way into the die. Operators use a sharper angle for strong metals to get the right shape.
- Springback is different for each metal. Stainless steel bends back more than copper or brass.
KRRASS Sheet Metal Bending Machines help operators fix springback. Their smart controls let users set the punch depth and die angle for each metal. This makes sure every bend is right, no matter what metal is used.
Press Brake Setup Tips

Best Practices
Operators get good results by following a simple setup. First, they pick the right tools for the metal and bend. The tools must fit the metal’s thickness and type. Next, they put all needed data into the machine’s controls. This means entering the punch and die sizes. Operators do a test run with scrap metal to check if the bend is correct before making real parts.
For best results, workers should:
- Put most bends in the center of the ram. This gives better power and control.
- Use tools that can handle the needed force.
- Press the tools lightly before tightening them.
- Make sure materials are clean, flat, and in the right spot.
- Follow the setup steps from the manufacturer.
KRRASS machines help with these steps. They have smart controls and easy instructions. Operators who use these tips make fewer mistakes and get better bends.
Mistakes to Avoid
Some mistakes can cause bad bends or damage. Operators may read instructions wrong and bend the metal the wrong way. Using the wrong tools can slow work and hurt the machine. Skipping setup or care makes bends less accurate.
Other mistakes are:
- Not checking alignment or calibration. This can mess up the bend angle. Laser tools help center the die.
- Using big dies on small machines. This can break parts or bend rails. The die should not be longer than the table by more than 200mm.
- Using the same V-die opening for every job. This can wear out the die. Operators should change the V-width for each metal.
Tip: Always check instructions and tools before starting a job.
Safety
Safety is always most important in a shop. Operators must know how the machine works and get training. They should warm up the machine when it is cold. Workers must hold the sheet straight and keep hands away from the bending area.
| Hazard Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Clamping or Cutting | Metal going into the bending area |
| Falling Object | Tools or metal dropping |
| Mechanical Movement | Getting pinched or crushed by moving parts |
| High Temperature | Sparks or heat causing burns |
| Electrical | Shock or fire from machine parts |
| Chemical | Bad gases or chemicals during bending |
| Operating Errors | Accidents from not knowing what to do |
| Equipment Failure | Accidents from not fixing machines |
Operators should wear safety gear and know how to stop the machine fast. KRRASS machines have safety features to help keep workers safe during every press brake job.
Maintenance
Taking care of a CNC press brake helps it work well for a long time. Operators who do regular maintenance have fewer problems and better bends. KRRASS suggests a simple plan that anyone can use.
Daily Maintenance Tasks:
- Clean the machine to get rid of dust and metal bits. Dirt can hurt moving parts.
- Check the hydraulic fluid level. If it is low, bending may not work right.
- Look for leaks near hydraulic lines and cylinders. Leaks can harm the machine and cause safety problems.
- Wipe the control panel and buttons. Clean controls help stop mistakes.
Weekly and Monthly Checks:
- Put oil on moving parts like the ram and bearings. Oil helps parts move easily and last longer.
- Make sure the back gauge moves smoothly. If it is not lined up, bends can be wrong.
- Look at the punch and die. Change tools that are worn or broken to keep bends good.
- Test the emergency stop and safety devices. Good safety systems keep operators safe.
Annual Deep Maintenance:
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Calibrate the machine | Makes sure bends are always correct |
| Inspect hydraulic pump pressure | Keeps bending force the same |
| Check electrical connections | Stops problems and keeps machine running |
| Review software and firmware | Updates controls for better use |
Operators should write down each maintenance task in a log. Keeping records helps track the machine’s health and plan future service.
Tip: Do maintenance when work is slow. This helps keep the press brake ready for busy times.
KRRASS machines have easy-to-read maintenance guides. These guides show each step for every task. Operators who use these guides help their machines work their best every day.
Regular care stops expensive repairs and makes sure every bend is good. A press brake that is well cared for is safe, works fast, and makes precise sheet metal parts.
Advanced Considerations

Springback
Springback can make bends less accurate in both air bending and bottom bending. When metal is bent, it tries to go back to its old shape. This can change the angle and size of the finished part. KRRASS machines have smart controls to help with springback. Operators use different ways to fix this problem:
- Bend the part a little more so it ends up at the right angle after springback.
- Do not make sharp bends in metals that spring back a lot.
- Make the bend bigger for soft metals to lower stress and get better results.
- Bend the part again if the first try is not right.
- Use more force to help the metal stay in its new shape.
CNC programming lets workers set exact bend depths and angles. The machine figures out how much to adjust for each type of metal. This helps workers get the right bend every time.
Tip: Operators should bend a test piece before making many parts. This helps them check if the springback fix is right.
Automation
Automation helps shops work faster and makes fewer mistakes on a cnc press brake. KRRASS uses smart automation to help workers do more in less time. Automated systems change bending settings as the job goes on. Sensors watch the process and make quick changes to keep every part correct.
- Automation makes jobs go faster and stops many human mistakes.
- The system cuts down setup time, so shops can finish jobs on time.
- CNC press brakes change settings for different metals to keep bends right.
- Sensors watch the bending and fix problems right away.
- Automation keeps every part just as accurate as the first one.
KRRASS uses these tools to help workers make good parts every time. Automation lets shops take on more work and keep their results steady.
Quality Control
Quality control helps make sure air bending and bottom bending are always precise. KRRASS machines support many ways to keep parts correct and reliable. Operators use tools and checks to look at every part.
| Quality Control Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Calibration of Tools | Operators check micrometers and calipers often to keep them correct. |
| Consistent Measurement Practices | Workers measure parts the same way each time to stop mistakes. |
| Advanced Design Implementation | Design software helps plan and see bends before making them. |
| Rigorous Quality Control Checks | Careful checks with calipers and micrometers make sure sizes and angles are right. |
| Visual Inspections | Operators look for surface problems using magnifying tools. |
| Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods | Special tests like ultrasonic or x-ray checks find hidden problems without hurting the part. |
| Documentation of Inspections | Workers write down check results to track quality and find problems early. |
CNC programming helps operators follow strict quality steps. KRRASS machines make it easy to check and save every bend. These steps help shops make parts that meet high standards.
Case Studies
Industrial Air Bending
Many factories use air bending because it is fast and flexible. Workers can make parts with different angles without changing tools. This saves time and lowers costs for companies. In one case, engineers used springback analysis with artificial neural networks (ANN). They wanted to guess how much the metal would bend back after forming. This helped them set the right process and made the bends more accurate.
Researchers also tried warm air bending on NM400TP steel. They heated the metal before bending it. This made the bending limit angle go up by 54%. The force needed to bend the metal was less than with cold air bending. This means workers could bend stronger metals with less effort. More teams now use process modeling for air bending. They test their computer models with real experiments. This helps them see how different settings change the final part. These new ideas make air bending a good choice for many factory jobs.
| Application | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Springback Analysis using ANN | Predicted springback, improved process accuracy |
| Warm Air Bending of NM400TP Steel | Increased bendability, reduced forming load |
| Process Modeling for Air Bending | Validated simulations, enhanced understanding of bending parameters |
Air bending lets factories change quickly and make good parts with fewer tool changes.
Precision Bottom Bending
Precision bottom bending is important for jobs that need exact shapes. Workers press the metal all the way into the die. This makes sharp and accurate angles. Every part matches the design because of this method. Car, plane, and electronics companies use bottom bending to meet strict rules.
Bottom bending stops most springback. The final angle stays close to what is needed. Workers get high accuracy and the same results every time. This makes the parts better. Bottom bending gives repeatable angles, so it is best for jobs where precision is very important. Many shops use bottom bending for making lots of the same part and for important pieces.
Precision bottom bending helps factories make parts that always meet customer needs.
KRRASS Success Stories
KRRASS has helped many customers make better sheet metal parts. One electronics company needed control panels with tight sizes. KRRASS gave them a press brake with smart controls and tools. The team made the same bends every time and wasted less metal.
A custom shop wanted to switch between air bending and bottom bending. KRRASS gave them a machine with quick-change tools and smart automation. Workers finished small and big jobs without waiting. The shop worked faster and met their deadlines.
KRRASS keeps helping customers with new ideas. Their machines help people get high accuracy, flexibility, and speed in every job.
Air bending is fast and flexible. Bottom bending is very accurate and gives the same results each time. These methods work best for different jobs. Operators pick air bending when they need to change things quickly. They use bottom bending when they want perfect bends. KRRASS makes press brakes with smart technology for all shops. Their machines help users make great bends. Try KRRASS products to make your sheet metal work better.
FAQ
What is the main difference between air bending and bottom bending?
Air bending leaves a space between the punch and die. This lets workers make many different angles. Bottom bending pushes the metal all the way into the die. It makes very exact angles and stops most springback.
Which method works best for high-volume production?
Bottom bending is best for making lots of parts. It gives the same results every time. This helps factories make many pieces that all match.
Can KRRASS machines perform both air bending and bottom bending?
KRRASS Sheet Metal Bending Machines can do both ways. Operators can change methods quickly. This helps them work with many jobs and materials.
How does springback affect the bending process?
Springback makes metal move back a little after bending. Workers must change the bend angle or use machine controls to fix this.
What materials can be bent using a CNC press brake?
Operators can bend steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Each metal bends in its own way. The machine and tools must fit the metal type.
Do operators need special training to use a CNC press brake?
Operators must learn how to use a CNC press brake. Training teaches setup, tool picking, safety, and checking part quality.
How often should maintenance be performed on a press brake?
Operators should clean and check the machine every day. They do bigger checks each week, month, and year. Regular care keeps the machine working well and makes good bends.
What safety features do KRRASS machines offer?
KRRASS machines have emergency stop buttons and safety guards. They also use sensors to keep workers safe and stop accidents during bending.