After many users buy back the press brake bending machine, they don’t know how to install and set up it. However, set up a press brake bending machine is a technich work...
Table of Contents
Importance of Setting Up Your Press Brake Efficiently
Throughout the entire setup process, no materials are created, and as setup time extends, the quantity of expenses continually increases. The efficiency and profitability of the press brake are determined by the number of accurate finished products that can be produced within a specific timeframe. If setup is too time-consuming, the time required to create each part decreases, leading to an increase in the price per part.
Utilizing similar setups to manufacture a large quantity of components is the only way to reduce the per-component cost on older hardware. Each operator should strive to master all quick setup techniques to produce more components at lower costs.
Steps For Setting Up Press Brake Bending Machine
Review Drawing
Initially, operators must acquaint themselves with the components. Examining the drawings is essential to ensure precision and the production of top-notch items. When operators scrutinize the drawing, they can readily grasp crucial particulars like material type, measurements, blank dimensions, flange tolerances, and inner angles' radii.
Eventually, operators must understand:
- Material type and density.
- Flange dimensions and tolerances.
- Required angles and angle tolerances.
- Inner arc of angles.
- Blank size.
In the absence of this data, supervisors may need to make educated assumptions. However, this increases the risk of inaccuracies in the part. Therefore, having detailed drawings is a crucial initial step.
Choose Tooling
The drawing aids in choosing the appropriate press brake tooling, offering several options: air bending, bottom bending, coinage, or customized applications.
For example, if the design specifies a bottoming tool and the inside arc length matches the material density.
With this particular machinery, it's advisable to utilize tooling that meets or exceeds the precision recommended by the tool maker. Even with precise press brake installation, worn equipment cannot produce accurate products.
Determine Tonnage
As an operator, accurately estimating tonnage requirements is crucial, particularly in air bending. Typically, tonnage charts are available for reference in air bending. For bottom bending, it's recommended to use approximately four times the tonnage required for air bending, while for coining, around eight times the air bending tonnage is ideal. Always consult the manufacturer's recommendations when utilizing special application tooling.
Press Brake Selection
If your workshop houses only one press brake, you may skip this step. However, if you have multiple brakes, ensure that you select the most suitable one for the task at hand.
Press brake machines typically have a tons-per-inch limit marked at the center. To determine the tons per inch for the brake, multiply the width across the lateral panels by 0.6, then divide the machine tonnage by your estimated value.
For a 12-inch-wide item, the maximum tonnage in the center of the machine should not exceed 25 tonnes. Exceeding 25 tonnes over 12 inches can result in overload, potentially damaging the ram permanently. When using tonnage control, whether manual or CNC, ensure to apply only the necessary amount of force to bend the part, avoiding surpassing the tonnage threshold at the center.
Additionally, it's important to note that overloading a press brake is permissible only when bottoming, coining, or utilizing specialty tooling for air bending.
Determine Tooling Position
It's crucial for the operator to verify whether the press brake manufacturer permits off-center loading. When operating off-center, it's essential to strictly adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines at all times.
Set Up Tooling
After determining the placement of the tooling on the bed, assemble the tooling and align the upper and lower tools to form the bend.
Among all the tasks in the setup process, tool installation typically requires the most time and resources.
If your brake is equipped with mechanical clamping bars, slightly release them to facilitate tool placement. Begin by installing the bottom tool (die) first, leaving it loosely positioned. Lower the ram to a position approximately 1/4 inch higher than the vertical position of the punch, just above the die.
Next, position the punch so that its tang is behind the clamping rods and slide it onto the die. During this step, the die bears the weight of the punch. Regardless of whether a safety label is present on the punch, follow the same procedure.
Lower the ram to seat the punch and position the die, then securely tighten the clamping bars around the tang. Finally, tighten the clamp rods and die set screws.
Using a hydraulic press brake bending machine with tooling can streamline and expedite this process, especially when snap tooling is utilized. Both functionalities can be retrofitted onto any press brake, enhancing efficiency further.
Programme Prese brake Machine
Programming the brake machine is the second most time-consuming step in the setup process, primarily due to the limited programming skills of most operators. Programming manual press brake machines can be laborious, time-intensive, and intimidating. In fact, programming a manual press brake often involves trial and error to ensure accuracy.
However, with a CNC press brake, programming is relatively straightforward. As a press brake operator, it's essential to invest time in researching and learning programming techniques to streamline the setup process. Alternatively, seeking assistance from an expert can help you quickly and easily grasp programming concepts.
Test Run
With all the preparations completed, it's time to perform a test bend. This step is crucial to verify that the machine is operating smoothly and that the setup is successful and accurate. Utilizing scrap metal for the test run is recommended to assess the bending process effectively.
Run The Parts
Once the correct setup is complete, you're ready to produce high-quality parts. However, it's important to acknowledge that not everything will always be flawless. Your supervisor will establish a testing and evaluation process for the components you produce.
Maintain consistency in your setup technique and apply it to each new component you create. Over time, your setup period will decrease, and your precision will significantly improve.
If you're seeking a trustworthy provider of press brakes, don't hesitate to reach out to KRRASS. With years of experience and hundreds of installed press brake machines worldwide, we are leaders in the industry.
Safety Precautions When Using A Press Brake Bending Machine
Potential risks during use
Clamping or Cutting Hazards: Clamping or cutting accidents can occur when a workpiece enters the bending area of a press brake, especially if the operator's hands or body parts enter the danger zone of the machine.
Falling object injury: When moving or adjusting the workpiece, the workpiece or tool may fall, causing injury to the operator.
Mechanical movement hazard: The mechanical moving parts of the bending machine such as the platen, mold and transmission device may cause crushing, pinching or impact injuries.
High Temperature Hazards: When using a press brake, high temperatures may be generated, such as sparks or heat from cutting and bending metal, which may cause fire or burn injuries.
Electrical Hazards: The press brake is powered by electricity, so there is an electrical hazard of electric shock, short circuit, or fire.
Chemical hazards: During the bending process, harmful gases or chemicals, such as metal oxides or waste liquids, may be produced, which may cause health hazards.
Danger of operating errors: If operators are not adequately trained or do not follow safe operating procedures, they may cause accidents, resulting in personal injury or equipment damage.
Danger of equipment failure: If the bending machine is not regularly maintained and inspected, it may malfunction or shut down unexpectedly, increasing the risk of accidents.
Safety precautions when using sheet metal bending machines
To ensure safe operation and achieve the desired output when using a sheet bending machine, it's crucial to adhere to basic safety norms. Here are some key guidelines:
Familiarize Yourself with the Machine:
Before using the sheet bending machine, take the time to understand its operation. If you're unfamiliar, refer to the instruction manual to grasp its functions thoroughly. Consider seeking training from experienced individuals to ensure safe handling.
Warm Up the Machine in Cold Weather:
In cold conditions, it's advisable to warm up the machine before use. Allow the machine to operate for a few minutes to ensure optimal performance and prevent stress on its components.
Ensure Proper Sheet Placement:
Correct placement of the sheet is essential for safe operation. Always hold the sheet parallel to the bender before initiating the bending process. Improper placement could result in the sheet hitting your body, leading to injuries.
Mindful Hand Placement:
Exercise caution when operating the bender to avoid hand injuries. Keep your hands away from the bending area while placing the sheet on the machine. Neglecting this precaution could result in severe accidents or permanent injuries.
By following these safety measures, you can mitigate the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment when using a press brake bending machine.
Sheet Metal Press Brake Tonnage Safety Rules
The tonnage selection of the press brake must match the thickness, bending shape and size of the metal plate to ensure safe and efficient operation. This information can usually be found in the tonnage table on the press brake.
Excessive tonnage may result in danger to the operator and damage to the workpiece and machine, so avoid selecting an overly large tonnage.
When selecting tonnage, also consider the length of the workpiece. It is best to choose a workpiece length that extends at least one-third of the table length to ensure adequate support and stability when maximum tonnage is reached.
Therefore, reasonable selection of the tonnage of the bending machine is crucial to ensure the safety of operators and avoid damage to the machine and workpieces.
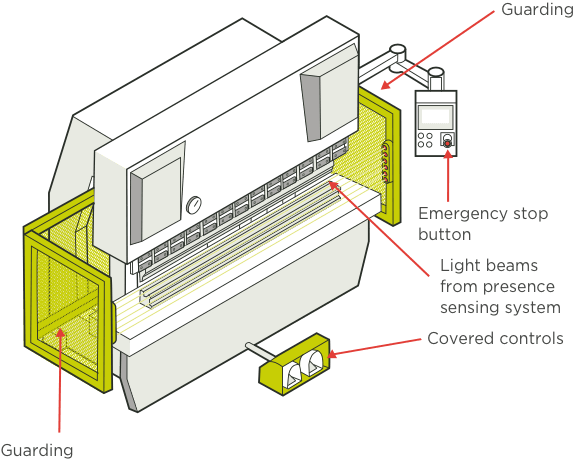
Press Brake Safety Device Expained
Press brake safety devices are essential components designed to ensure the safe operation of press brakes, which are commonly used in metalworking industries for bending and forming sheet metal. These devices help to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries by protecting operators from hazards associated with the machine's moving parts and processes. Here are some commonly used press brake safety devices explained:
Light Curtain
The press brake light curtain is a commonly used photoelectric safety device used to protect operators from injury during the operation of the press brake. Light curtains are typically installed around the bending area of a press brake, creating an invisible beam barrier. When an object (such as the operator's hand or body) enters the beam area, the light curtain will immediately detect it and quickly stop the operation of the bending machine to prevent accidents.
Press brake light curtains usually consist of two parts: transmitter and receiver. The transmitter generates an infrared beam and transmits it to the receiver. The receiver receives the beam and monitors whether the beam is interrupted. If the light beam is interrupted, it means that an object has entered the range of the light curtain. At this time, the light curtain will send a signal to stop the bending machine immediately.
Two-Hand Controls
Two-hand press brake control is a safety feature designed to prevent accidents by requiring both hands to be activated simultaneously to operate the machine. Two-hand controls typically consist of two buttons or switches located a certain distance apart on the machine's control panel.
The operator must press both buttons simultaneously and maintain continuous pressure in order for the press brake to operate. Releasing one or both hands will immediately stop the machine.
Many safety regulations and standards require the use of two-hand controls on potentially hazardous machinery, including press brakes. Implementing two-hand controls helps businesses comply with these regulations and creates a safer work environment for employees.
Safety Barriers
The side guards of a press brake serve as adjustable barriers situated on both sides of the machine. These guards play a crucial role in safeguarding operators by preventing access to the work area or rear gauge from either side, thus significantly reducing the risk of hand injuries.
Similarly, the rear guard acts as a protective barrier, effectively blocking access to the rear of the machine. By doing so, it prevents operators from inadvertently contacting the rear gauge, minimizing the potential for accidents and injuries.
Additionally, the press brake's housing and interlocking press barrier can be strategically positioned at a safe distance. This positioning serves to protect both the machine and the operator from any personnel or objects that may come into proximity, mitigating the risk of damage to the equipment and injury to individuals. These safety measures collectively contribute to fostering a secure working environment and promoting accident prevention in press brake operations.
Safety PLC
A safety PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for a bending machine is a special type of PLC designed to monitor and control the safety-related functions of the machine. This device continuously monitors various safety devices and sensors installed on the press brake, such as light curtains, two-hand controls, emergency stop buttons and safety mats. It checks for any unusual or unsafe conditions in real time.
Safety PLC executes safety-related logic and algorithms to ensure safe operation of the bending machine. It processes inputs from safety devices and implements predefined safety functions such as emergency stops, machine shutdowns and interlocks.
In the event of an emergency or dangerous situation, the safety PLC triggers a safe stop sequence, bringing the press brake to a controlled stop to prevent accidents and injuries. After the safety hazard is resolved, the safety PLC is responsible for managing the safe restart of the machine.
It plays a key role in ensuring the safe operation of machines by monitoring, controlling and coordinating various safety functions.
Conclusion
Consistently applying your setup techniques to every new element you create will simplify your setup process and significantly improve your accuracy over time.
For reliable press brake solutions, consider contacting KRRASS. With years of experience and a track record of successfully installing hundreds of press brakes around the world, we are an industry leader in providing high-quality equipment and exceptional service.