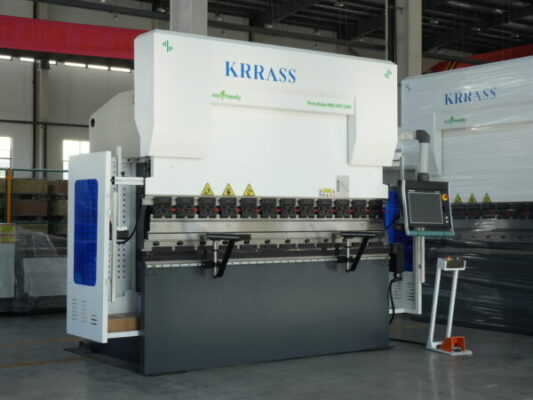
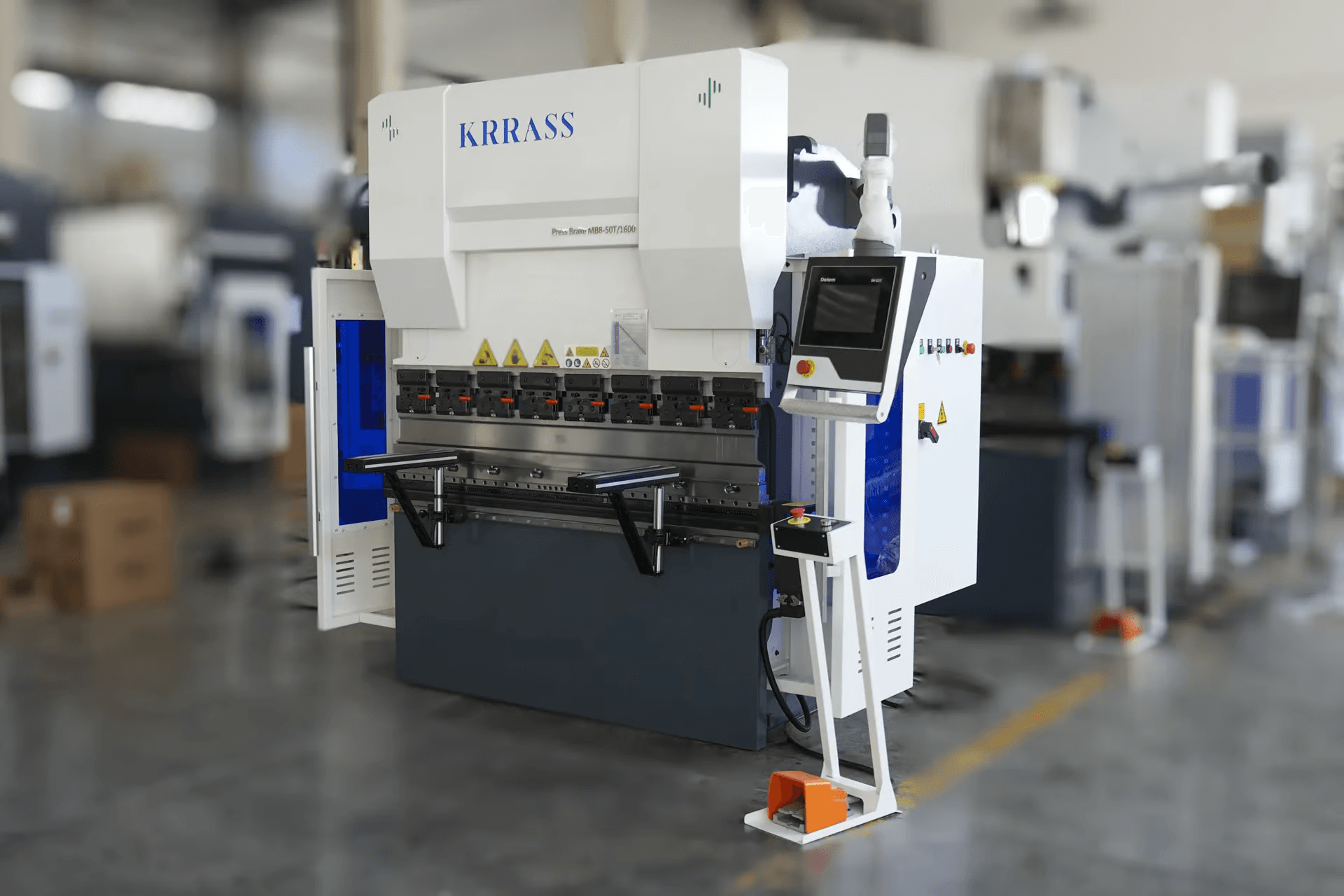
Small CNC press brakes have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering an efficient and cost-effective solution for small businesses. These compact machines combine the precision of computer numerical control (CNC) with the versatility needed to handle a wide range of bending operations. For small businesses aiming to maximize productivity while minimizing operational costs, investing in a small CNC press brake can significantly enhance their capabilities. With their user-friendly interfaces and space-saving designs, these machines are ideally suited for environments where efficiency and accuracy are paramount.
Introduction
What Is A CNC Press Brake
CNC press brakes are advanced machines used in metal fabrication to bend and shape sheet metal with precision and efficiency. These machines utilize computer numerical control (CNC) technology to automate the bending process, ensuring high accuracy and repeatability. Unlike traditional press brakes, CNC press brakes can be programmed to perform complex bends with minimal manual intervention, making them an essential tool in modern manufacturing.
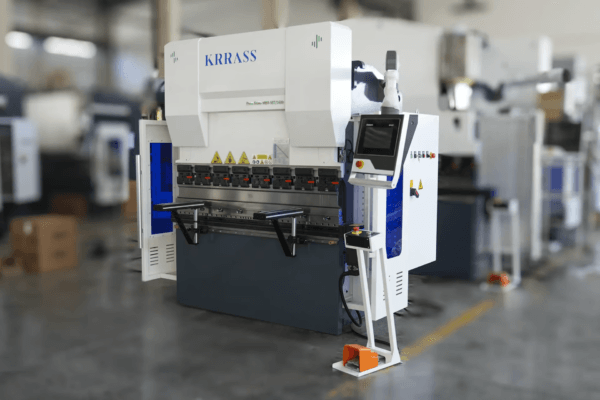

What Is A Small CNC Press Brake
Small CNC press brakes are favored by small to medium-sized workshops or businesses that require flexibility, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in their bending operations. They provide a balance between capability and space efficiency, making them a practical choice for a wide range of bending applications.
Beyond its compact footprint, a small CNC press brake integrates seamlessly into limited workspaces, optimizing operational efficiency without compromising on performance. These machines are adept at handling moderate bending tasks, typically accommodating bending lengths up to 3 meters and exerting forces ranging from 20 to 100 tons, depending on specific models and configurations. This versatility extends to diverse applications, from fabricating small parts with intricate geometries to executing precise bends required in specialized industries like electronics, automotive, and signage.
Importance of Efficiency in Small Businesses
For small businesses, efficiency is crucial to staying competitive and profitable. Limited resources and smaller workspaces mean that every piece of equipment must contribute to streamlined operations and optimized production. Efficient machines reduce labor costs, minimize material waste, and enhance overall productivity, enabling small businesses to deliver high-quality products while maintaining tight margins.
Key Features of Small CNC Press Brakes
Small CNC press brakes are specifically designed to meet the needs of small businesses and workshops. These compact machines combine the precision and capabilities of larger CNC press brakes with a size that fits more constrained spaces. Despite their smaller footprint, they do not compromise on performance, offering the same level of accuracy and versatility. Small CNC press brakes are an excellent investment for businesses looking to enhance their fabrication capabilities without the need for extensive space or significant capital outlay.
Key Features of Small CNC Press Brakes
Compact Design and Space-Saving Benefits
Small CNC press brakes are engineered with a compact design, making them ideal for small businesses with limited floor space. Their space-saving benefits allow these machines to fit into tighter workspaces without sacrificing performance, enabling businesses to maximize their production areas effectively.
Precision and Accuracy in Bending Operations
One of the standout features of small CNC press brakes is their ability to perform highly precise and accurate bending operations. The integration of advanced CNC technology ensures that each bend is executed with exacting precision, reducing material waste and ensuring consistent quality in every project. When it comes to selecting a reliable and efficient small CNC press brake, Krrass stands out as a leading brand. Known for their innovative designs and robust engineering, Krrass small CNC press brakes deliver exceptional performance, helping businesses achieve optimal results with ease.
User-Friendly Interface and Controls
Small CNC press brakes are equipped with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making them accessible even to operators with limited experience. The easy-to-navigate control panels streamline the setup and operation processes, minimizing the learning curve and enhancing overall productivity.
Versatility in Handling Different Materials and Thicknesses
These machines are designed to handle a diverse range of materials and thicknesses, providing small businesses with the versatility needed to take on various projects. Whether working with thin sheets of metal or thicker, more robust materials, small CNC press brakes deliver reliable performance, making them a valuable asset for any manufacturing environment.

General Specification of Small CNC Press Brakes
Bending Capacity
Maximum bending length: Usually ranges from 1 meter (approximately 3 feet) to 3 meters (approximately 10 feet) or more.
Maximum bending thickness: Typically ranges from 1 mm (0.04 inches) to 6 mm (0.24 inches) for mild steel, depending on machine strength.
Pressing Force
Force exerted by the press brake: Often ranges from 20 tons to 100 tons or more, depending on the model and application requirements.
Back Gauge System
Precision back gauge with multiple fingers for accurate positioning of the material, often controlled by CNC for automated setup and operation.
Differences Between Small and General CNC Press Brake
Small CNC Press Brake
Small CNC press brakes are characterized by their compact size and lower capacity compared to general CNC press brakes. Typically occupying less floor space and offering a maximum bending length of up to 3 meters (approximately 10 feet) and a maximum bending force of around 20 to 100 tons, these machines are ideal for smaller workshops or businesses with moderate bending needs. They excel in bending thinner materials and smaller parts where precision and flexibility are crucial.
Despite their smaller size, modern small CNC press brakes often feature advanced CNC controls, back gauge systems for accurate positioning, and necessary safety features, making them suitable for precise and efficient bending operations in constrained environments.

General CNC Press Brake
In contrast, general CNC press brakes are larger and more robust, designed to handle larger sheet sizes, heavier materials, and higher production volumes. With a typical bending length exceeding 3 meters and a bending force exceeding 100 tons, these machines are favored in medium to large-scale production environments requiring versatility and high throughput.
They offer advanced features such as multi-axis CNC controls, extensive tooling options, automatic tool changers, and sophisticated back gauge systems. General CNC press brakes cater to a wide range of industries and applications, providing flexibility for diverse bending requirements and integrating seamlessly with other manufacturing processes.
Advantages of CNC Press Brake for Small Businesses
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Larger Machines
Small CNC press brakes typically cost between $30,000 to $80,000, whereas larger industrial models can range from $100,000 to over $500,000. This significant cost difference makes small CNC press brakes a more affordable option for small businesses looking to invest in bending capabilities without a large capital outlay. For example, a small fabrication shop in Ohio reduced their initial equipment costs by 40% by choosing a compact CNC press brake over a larger industrial model.
Reduced Labor Costs Due to Automation
Automation in small CNC press brakes drastically reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for skilled operators to oversee bending operations. On average, businesses can save up to 30% on labor expenses annually. For instance, a metalworking company in California cut down their labor costs by 25% after implementing a small CNC press brake, allowing their operators to focus on more specialized tasks such as quality control and design.
Increased Production Speed and Efficiency
Small CNC press brakes can bend up to 40 sheets per hour, compared to manual methods that typically handle around 10 sheets. This accelerated production capability not only boosts output but also improves overall project turnaround times by up to 50%. For example, a workshop in Texas doubled its production capacity within the first six months of using a small CNC press brake, meeting growing customer demands without compromising on quality.
Lower Maintenance Requirements
Small CNC press brakes require minimal maintenance compared to larger machines, with annual upkeep costs averaging around $2,000 to $5,000. This lower maintenance requirement translates to fewer downtimes and reduced operational disruptions. For instance, a fabrication business in Florida reported a 30% decrease in maintenance-related downtime after switching to a small CNC press brake, allowing them to fulfill orders more efficiently and maintain high customer satisfaction levels.
Applications in Various Industries
Small CNC press brakes find versatile applications across several industries, owing to their compact size, precise bending capabilities, and cost-effective operation. Here are some key sectors where these machines are widely utilized:
1. Automotive Industry
Small CNC press brakes are essential in the automotive sector for manufacturing components such as brackets, panels, and frames. Their ability to bend sheet metal with high precision ensures that parts meet strict quality standards while maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
2. Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense, where precision and reliability are paramount, small CNC press brakes play a crucial role in fabricating components for aircraft and military equipment. These machines handle a variety of materials, including aluminum and titanium, to exact specifications required for aerospace applications.
3. Metal Fabrication
Small CNC press brakes are indispensable in general metal fabrication shops. They are used to create custom parts and assemblies for a wide range of industries, from electronics and appliances to furniture and signage. Their versatility in handling different materials and thicknesses makes them adaptable to various fabrication needs.
4. Electronics and Telecommunications
In the electronics industry, small CNC press brakes are utilized to manufacture enclosures, chassis, and mounting brackets for electronic devices and telecommunications equipment. The precise bending capabilities ensure that components fit together seamlessly and meet the stringent requirements of electronic assembly.
5. Construction and Architecture
Small CNC press brakes are employed in the construction and architectural sectors to fabricate structural components, decorative elements, and facades. Their ability to create complex bends and shapes allows architects and builders to realize unique designs while maintaining structural integrity and durability.
6. Medical Equipment
In the medical field, small CNC press brakes are used to produce components for medical devices, equipment enclosures, and surgical instruments. The machines' ability to work with stainless steel and other medical-grade materials ensures compliance with strict regulatory standards for hygiene and safety.
7. Renewable Energy
Small CNC press brakes play a role in the renewable energy sector by fabricating components for solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. These machines contribute to the production of renewable energy infrastructure by manufacturing parts that are durable and weather-resistant.
8. Small Business Workshops
Finally, small CNC press brakes are ideal for small business workshops and startups looking to expand their manufacturing capabilities without investing in large, costly machinery. These machines enable entrepreneurs to offer custom fabrication services and meet customer demands efficiently.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Small CNC Press Brake
Material Types and Thickness
Material Types: Determine the types of materials your business processes, such as stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel, and others. Each material has different characteristics that affect bending, such as tensile strength and elasticity.
- Stainless Steel: Typically ranges from 0.5 mm to 6 mm thickness for sheet metal fabrication.
- Aluminum: Commonly processed in thicknesses from 0.8 mm to 8 mm.
- Mild Steel: Often bent in thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to 10 mm.
Tonnage Requirements: The thickness and material type directly impact the tonnage capacity needed from the press brake. Higher tensile strength materials like stainless steel require higher tonnage to achieve precise bends without deformation.

Evaluating Machine Specifications
Tonnage Capacity: Select a press brake with adequate tonnage capacity to handle the maximum thickness and material type you work with. Tonnage directly impacts the machine's ability to bend material effectively without strain or deformation.
Bed Length and Depth: The bed length determines the maximum length of material that can be bent, while the depth (throat depth) affects the distance from the edge of the material to the bend line. Choose dimensions that accommodate your typical sheet sizes and bending requirements.
Backgauge System: An accurate and versatile backgauge system is crucial for positioning material consistently during bending operations. Look for press brakes with programmable backgauges that offer multi-axis control to handle complex bending sequences.
Importance of After-Sales Support and Warranty
Technical Support: Ensure the manufacturer provides comprehensive technical support, including installation, training for operators, and troubleshooting assistance. Prompt technical support minimizes downtime and ensures smooth operation.
Warranty Coverage: Review the warranty terms and coverage offered by the manufacturer. A robust warranty protects your investment against defects in materials or workmanship, providing peace of mind and financial security.
Availability of Spare Parts: Check the availability of spare parts and their cost. Opt for a manufacturer or distributor that maintains a stock of critical components to expedite repairs and minimize downtime.
Comparing Different Brands and Models
Brand Reputation and Reliability: Research the reputation of different brands within the industry. Seek feedback from other users and industry experts to gauge reliability, durability, and overall satisfaction with the equipment.
Technology and Innovation: Evaluate the technological features and innovations incorporated into each press brake model. Look for advancements in CNC controls, safety features, energy efficiency, and automation capabilities that align with your operational goals.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO beyond the initial purchase price. Factor in maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential productivity gains to assess the long-term value and return on investment (ROI) offered by each press brake.
Customization Options: Some manufacturers offer customization options to tailor the press brake to specific operational needs or industry requirements. Assess whether customization options are available and how they can enhance the machine's suitability for your business.
By conducting a thorough evaluation based on these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing a small CNC press brake that enhances productivity, meets quality standards, and supports the growth of your business effectively.
Top 10 Brands of Small CNC Press Brakes
- Amada
- Trumpf
- Bystronic
- Accurpress
- Durma
- Haco
- LVD
- Baykal
- SafanDarley
- Krrass
These brands are well-regarded for their technological advancements, robust construction, precision engineering, and comprehensive after-sales support, making them popular choices among manufacturers seeking high-performance small CNC press brakes. When considering a purchase, evaluating the specific features, reputation, and customer reviews of these brands can help you find the best fit for your business's needs.
Maintenance and Care Tips for Small CNC Press Brakes
Daily Maintenance Routine
Visual Inspection: Conduct a daily visual inspection before operating the press brake. Look for signs of wear, loose bolts, hydraulic leaks, and any abnormalities in the machine's operation.
Cleanliness: Keep the press brake and its surroundings clean from dust, debris, and metal shavings. Regularly vacuum or wipe down the machine, tooling, backgauge, and work area to prevent buildup that can affect precision and safety.
Lubrication and Hydraulic System Care
Lubrication Schedule: Follow the manufacturer's recommended lubrication schedule for all moving parts, including ball screws, guides, bearings, and hydraulic components. Use the specified lubricants to ensure smooth operation and prevent premature wear.
Hydraulic System Maintenance: Monitor hydraulic fluid levels regularly and inspect for leaks in hoses, fittings, and seals. Replace hydraulic fluids as recommended by the manufacturer and address any leaks promptly to prevent system failures.
Tooling and Bed Maintenance
Tooling Inspection: Regularly inspect punches, dies, clamps, and other tooling components for wear, cracks, or damage. Replace worn-out or damaged tooling to maintain bending accuracy and avoid material defects.
Bed and Backgauge Alignment: Ensure the bed and backgauge are properly aligned according to manufacturer specifications. Misalignment can affect bend accuracy and consistency.
Electrical and Control System Checks
Electrical Components: Inspect electrical connections, wiring, and control panels for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Keep control panels clean and free of dust to prevent electrical issues and ensure reliable machine operation.
Software Updates: Stay updated with software and firmware upgrades provided by the manufacturer. These updates often include improvements in performance, safety features, and compatibility with new technologies.
Operator Training and Safety Practices
Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training for operators on machine operation, safety protocols, and maintenance procedures. Well-trained operators can identify potential issues early and operate the machine safely and efficiently.
Safety Checks: Regularly check and maintain safety features such as light curtains, emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and guarding. Ensure operators adhere to safety guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries.
Scheduled Maintenance and Service
Maintenance Schedule: Establish a regular maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and machine usage. Schedule routine inspections, lubrication, and servicing to prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of critical components.
Professional Servicing: Engage qualified technicians for annual or bi-annual maintenance checks and servicing. They can perform detailed inspections, adjustments, and repairs to ensure the press brake operates at peak performance.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintenance Logs: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and service history. Documentation helps track machine performance, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance effectively.
Comparison of Small CNC Press Brakes and Traditional Press Brakes
Small CNC Press Brakes
1. Automation and Precision:
- CNC Control: Small CNC press brakes are equipped with sophisticated CNC systems that automate the bending process. Operators program the machine to perform precise bends with consistent angles and dimensions.
- Accuracy: CNC technology ensures high precision, reducing variability in bend angles and minimizing material scrap. This accuracy is crucial for industries requiring tight tolerances, such as aerospace and automotive.
2. Versatility and Flexibility:
- Programming Capabilities: CNC press brakes can store a wide range of bending programs, allowing for flexibility in handling diverse part geometries and material types.
- Quick Setup: Once programmed, setup times are reduced significantly compared to traditional methods. This efficiency is beneficial for handling frequent changeovers and small batch sizes efficiently.
3. Productivity and Efficiency:
- Faster Cycle Times: CNC press brakes operate at faster cycle times due to automated bending sequences and tooling setups. This leads to higher productivity and throughput.
- Multi-Axis Control: Advanced CNC models offer multi-axis control, enabling simultaneous adjustment of backgauges, crowning systems, and tooling angles. This capability enhances overall production efficiency.
4. Operator Skill Requirements:
- Training Needs: Operators require training in CNC programming and operation. Once trained, they can handle complex bending tasks with ease, leveraging the machine’s automation capabilities.
- Reduced Labor Intensity: CNC automation minimizes manual labor involved in setup and operation, freeing up operators for more skilled tasks and reducing ergonomic strain.
5. Integration with CAD/CAM Systems:
- CAD Compatibility: CNC press brakes integrate seamlessly with CAD/CAM software, allowing direct programming from digital designs. This integration streamlines the workflow from design to manufacturing, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency.
Traditional Press Brakes
1. Manual Operation and Control:
- Manual Adjustments: Traditional press brakes rely on manual adjustments for setting up tooling, backgauges, and bending sequences.
- Operator Skill: Skilled operators are crucial for accurate setup and operation, manually adjusting parameters for each bending operation.
2. Suitability for Simple Bending Tasks:
- Basic Operations: Traditional press brakes excel in straightforward bending tasks and are suitable for low to medium production volumes where setup times are less critical.
- Limited Automation: Lack of automation limits their suitability for handling complex part geometries and high-volume production runs efficiently.
3. Setup and Changeover Times:
- Longer Setup Times: Setup and changeover times are typically longer compared to CNC press brakes due to manual adjustments and measurements.
- Batch Size Flexibility: Adjusting for varying batch sizes requires manual recalibration of tooling and settings, which can prolong setup times and decrease operational efficiency.
4. Cost Considerations:
- Initial Cost: Traditional press brakes may have a lower initial purchase cost compared to CNC models, making them more accessible for smaller operations or specific applications.
- Operating Costs: Higher labor costs associated with manual operation and setup may impact overall operating costs over time, especially for higher production volumes.
What Are Small CNC Press Brakes Cost
The cost of small CNC press brakes can vary based on several factors such as brand, size, features, and where you purchase them. Here’s a rough estimate to give you an idea:
Entry-Level Models: These typically range from $20,000 to $50,000 USD. These may have basic features suitable for lighter duty work or smaller shops.
Mid-Range Models: These can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $100,000 USD. They often offer more advanced features, higher precision, and may be suitable for more frequent or varied production needs.
High-End Models: These can exceed $100,000 USD and can go up significantly depending on the size and capabilities of the press brake. They are typically used in larger production facilities requiring high precision and automation.
Basic Paramters of Small CNC Press Brake (From Krrass)
| No. | Item | Unit | 40T/1500 |
| 1 | Bending force | kN | 400 |
| 2 | Bending length | mm | 1500 |
| 3 | Columns distance | mm | 1200 |
| 4 | Throat depth | mm | 300 |
| 5 | Cylinder stroke(Y1,Y2) | mm | 150 |
| 6 | Die loading height(Daylight) | mm | 380 |
| 7 | Y-axis down speed | mm/sec | 150 |
| 8 | Y-axis return speed | mm/sec | 120 |
| 9 | Y-axis wording speed | mm/sec | 4~15(adjustable) |
| 10 | Y-axis accuracy | mm | ±0.01 |
| 11 | Work-piece linearity | mm | 0.3/m |
| 12 | Max.Back gauge distance | mm | 500 |
| 13 | X-axis (R-axis) speed | mm/sec | 400 |
| 14 | X-axis (R-axis) accuracy | mm | ±0.01 |
| 15 | Front sliding arms | pcs | 2 |
| 16 | Bending angle accuracy | (') | ≤±18 |
| 17 | Back gauge finger stopper | pcs | 4 |
| 18 | Main motor | KW | 5.5 |
| 19 | Dimension | Length(mm) | 1700 |
| Width(mm) | 1450 | ||
| Height(mm) | 2200 | ||
| 20 | Weight | kg | 3500 |