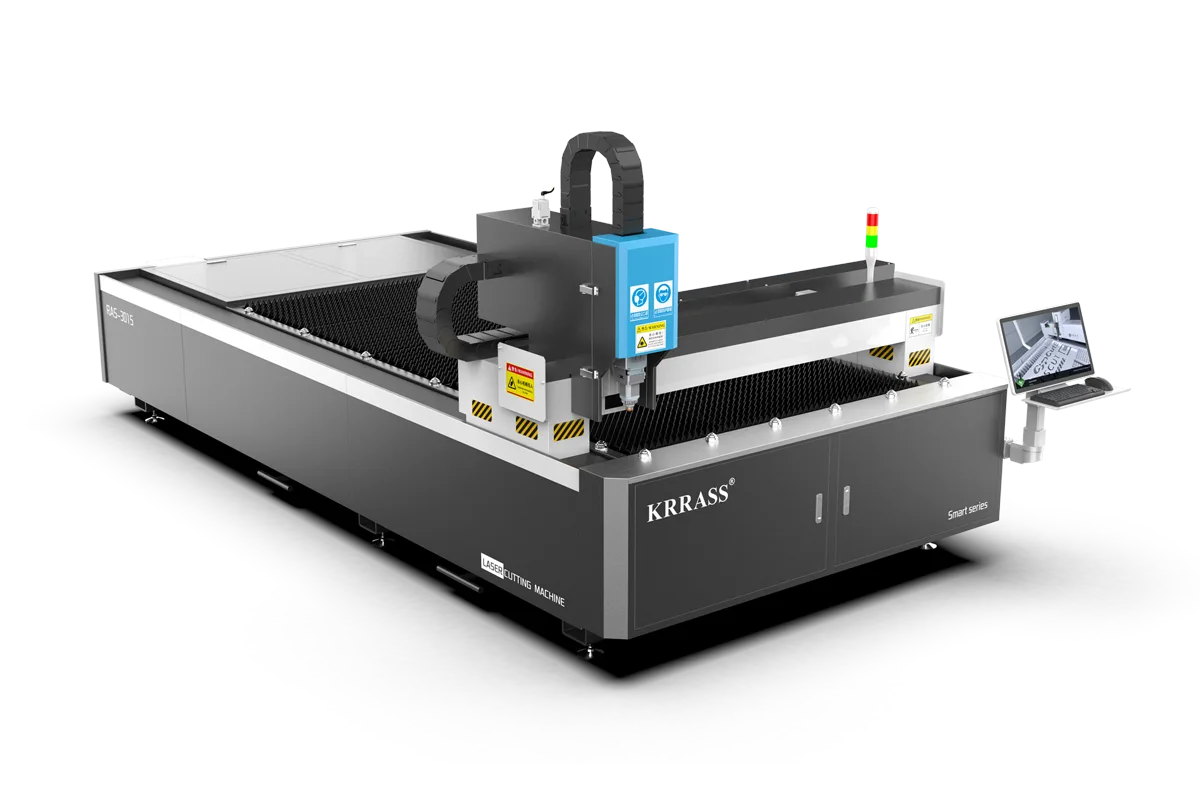
When you are searching for sheet metal laser cutting machine, there are always a variety of choices in the market. In fact, choosing a suitable laser cutting machine is not an easy task. You need to consider the initial cost of the machine itself, including the laser, cutting head, cutter system, etc.
This article will help you solve the problems of laser cutting machines from multiple practical perspectives, thereby helping you save costs and choose the best laser cutting machine solution.
Origin of Laser Cutters
The history of laser cutting dates back to 1917 when Albert Einstein proposed the theory of "stimulated emission of radiation," which is the fundamental principle behind modern lasers. Einstein theorized that electrons could emit photons when they absorbed sufficient energy to move up an energy level within an atom.
The First Working Laser
In 1959, scientist Gordon Gould expanded on Einstein's theory. He suggested that stimulated emission of radiation could be used to amplify light, leading to the acronym LASER, which stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
In 1960, Theodore Maiman created the first working laser in a California laboratory using synthetic ruby to generate a deep red beam. Although initially met with skepticism and described as "a solution looking for a problem," Maiman's invention captured the interest of many scientists, including those at Bell Labs in New Jersey.
Development of Laser Cutting Techniques
It wasn't until 1964 that thermal cutting techniques using lasers were developed. Kumar Patel, a scientist at Bell Labs, invented a gas laser cutting process using a carbon dioxide mixture, which proved to be a faster and more cost-effective improvement over ruby laser cutting. Later that year, Patel's colleague, J.E. Geusic, invented the crystal laser process.
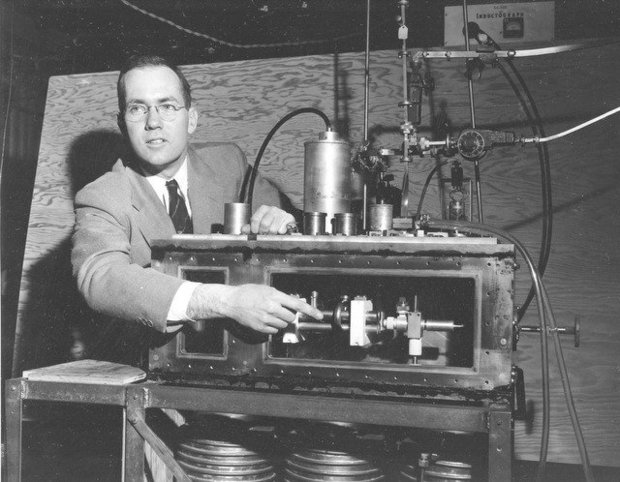

The potential of laser technology soon captured the public imagination, most notably featured in the 1964 film "Goldfinger," where the villain attempts to cut James Bond in two with a laser beam. This iconic scene helped bring laser cutting technology into the spotlight, highlighting its dramatic and practical potential.
What Is A Sheet Metal Laser Cutting Machine
A sheet metal laser cutting machine uses a high-powered laser beam to cut, etch, burn, vaporize, or melt away materials. The machine is a type of CNC (Computer Numerical Controlled) machine that uses a computer program to control the laser beam's movement. The laser's output is directed through optics to focus and redirect a powerful, consistent light until it reaches a fine point. When the light is concentrated enough, it becomes extremely hot, allowing it to cut through materials.
Laser cutting machines can be used in a variety of industries, including engineering, industrial manufacturing, and precision cutting. They can process almost any material, including metals, plastics, wood, acrylic, carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, cork, and leather. Laser cutting machines can also recreate designs made on a computer with great accuracy, even if they involve large numbers of curves and angles.

What Is Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a technique used to cut or engrave hard materials by burning, melting or vaporizing. The process has multiple industrial applications across various industries and can be used to drill holes or cut shapes in metal and other materials on a production line. Laser cutting is also used as an artistic technique to engrave decorative designs on surfaces.The primary advantage of laser cutting technology is its accuracy, and the high power beam is concentrated through a laser cutting nozzle for pinpoint accuracy. Modern laser cutting generally uses CAD technology, allowing artists and engineers to create intricate designs with an industrial laser.
How Does Laser Cutting Work
A laser functions by energizing atoms within a solid, liquid, or gas medium using an energy pump, which can be an electrical current or another laser. When these atoms absorb energy, they emit light. This light is then concentrated by mirrors placed at each end of the medium, forming an optical cavity. In laser cutting, the laser beam is focused onto sheet metal or other hard materials. Technicians use mirrors, lenses, and compressed gases like carbon dioxide to adjust the laser beam's focus through a cutting nozzle. The concentrated beam melts or burns away the material, and the cutting head or the material itself can be moved to the next cutting area. CAD technology automates the movement of the laser head over the cutting surface, ensuring precise and efficient cutting of the sheet metal or other materials.
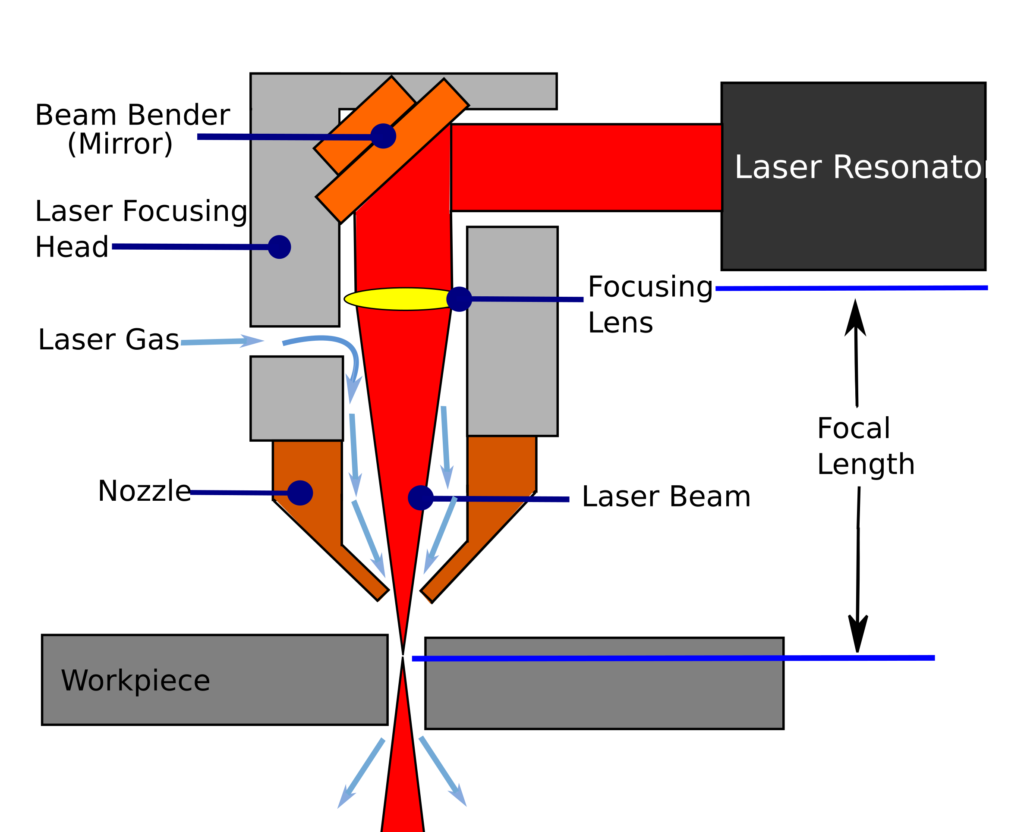
Applications of Sheet Metal Laser Cutter
- Automotive Industry:
- Aerospace Industry:
- Electronics Industry:
- Construction Industry:
- Medical Industry
Three Sheet Metal Laser Cutting Process
1. Laser Beam Fusion Cutting
The laser beam fusion cutting process uses an inert gas, mostly nitrogen. The low-reaction process gas continuously vaporizes the cutting gap of the material. As the molten material gets removed, inert gas prevents oxidation at the cutting edge without interfering with the process.
This laser cutting method is suitable for cutting flat, thin sheets of aluminum alloys and stainless steel that require high aesthetic appeal and fewer finishing operations.
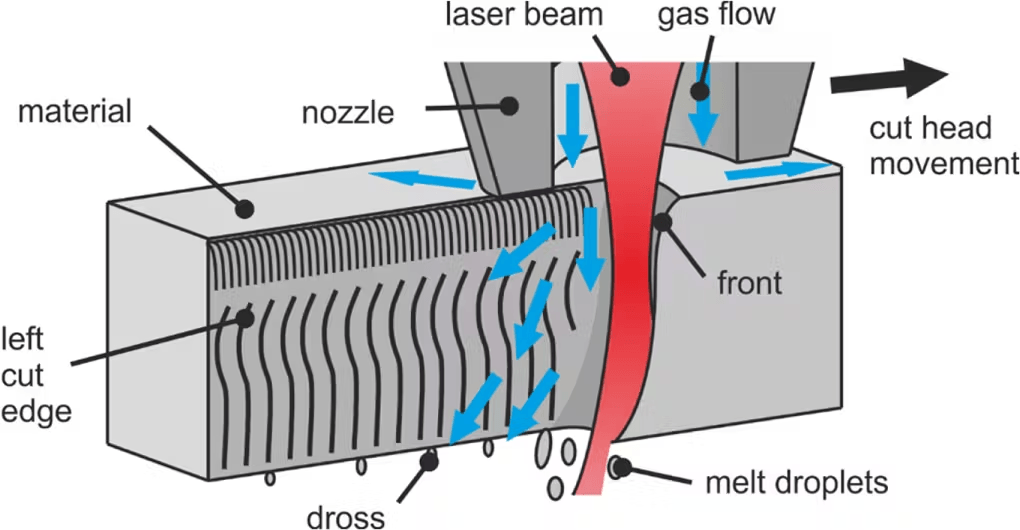
2. Laser Beam Sublimation Cutting
As the name suggests, laser beam sublimation cutting evaporates the material. Instead of melting the material like other laser cutting processes, they are immediately changed from solid to gas – sublimation.
Like fusion cutting, laser beam sublimation cutting uses inert gases to blow the material’s vapor out of the kerf. So, there are no oxidants on the cutting edge. It is often used in cutting organic materials like wood, leather, textiles, etc.
3. Laser Beam Flame Cutting
Laser beam flame cutting uses a combustible gas – oxygen to thrust out the molten material. The laser heats the workpiece creating spontaneous combustion after melting the material. The oxygen gas provides more energy for the cutting process through oxidation – an exothermic reaction.
Flame cutting is ideal for cutting mild steel and fusible materials such as ceramics. This cutting process may cause burns on the cutting surface since the gas is an oxidant. Proper optimization of the process parameters will help prevent the formation of burrs.
Pros & Cons of Sheet Metal Laser Cutting
Pros
- High-Precision and Accuracy
- Automated Process
- Damage Prevention
- Compatible With Most Materials
Cons
- Requires Technical Operator
- Limitations to Metal Thickness
- Release of Harmful Fumes and Gases
- High Initial Investment
Types of Laser Cutters and Applicable Materials
1. CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers are one of the most common types of laser cutters, known for their efficiency and versatility. They are ideal for cutting, engraving, and boring a variety of materials, including:
- Wood
- Paper
- Plastics
- Glass
- Textiles
- Leather
CO2 lasers operate using a gas mixture primarily composed of carbon dioxide, which is electrically stimulated to produce the laser beam. These lasers are particularly effective for non-metallic materials and can achieve high precision at relatively low costs.
2. Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are another widely used type of laser cutter, especially in industrial settings. They utilize a solid-state laser source, where the laser beam is generated by a seed laser and amplified within a glass fiber. This type of laser is highly efficient and suitable for:
- Metals (including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass)
- Plastics
- Ceramics
Fiber lasers are known for their high cutting speeds and excellent beam quality, making them ideal for detailed and intricate cutting tasks. They are also more energy-efficient compared to CO2 lasers and have a longer operational life.
3. Nd Lasers
Nd (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) lasers are solid-state lasers that produce a high-intensity beam, suitable for applications requiring deep penetration and high power. They are commonly used for:
- Metal engraving
- Deep metal cutting
- Marking various hard materials
Nd lasers are preferred for tasks that demand high precision and power, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. These lasers can also be used for welding and drilling.
4. Diode Lasers
Diode lasers are compact and cost-effective, often used in smaller, less industrial applications. They are suitable for:
- Engraving
- Marking
- Cutting thin materials
Diode lasers are less powerful than CO2 and fiber lasers but are useful for detailed work on small projects and are often used by hobbyists and small businesses.
Core Parts of Sheet Metal Laser Cutters
1. Fiber Laser Source
It is the most core component of fiber laser cutting machine, and it is also the “power source” for fiber laser cutting machine to realize cutting operation. Compared with other types of lasers, fiber lasers have the advantages of higher efficiency, longer service life, less maintenance, and lower cost. Laser is the core "power source" in a laser equipment. Like car engine, it is also a relatively expensive part of fiber laser cutting machine.
Imported fiber laser brands on the market currently include German IPG, Rofin and British SPI. With the development of science and technology, Chinese laser brands such as Raycus and Max continue to emerge, and are gradually recognized by the market for their high cost performance. If you want to know the difference between different brands of lasers, please read on.
2. Cutting Head
The cutting head is the laser output device of the fiber laser cutting machine, which consists of a nozzle, a focus lens and a focus tracking system. The cutting head of the laser cutting machine travels according to the set cutting track, but the height of the laser cutting head needs to be adjusted and controlled according to different materials, thicknesses and cutting methods.
3. CNC System
The control system is the main operating system of the fiber laser cutting machine. It mainly controls the machine tool to realize the movement of X, Y, Z axis, and at the same time controls the output power of the laser. Its quality determines the stability of the working performance of the fiber laser cutting machine. Through the accurate control of the software, the cutting accuracy and cutting effect can be effectively improved.
Here list world most popular CNC system munufactures for fiber laser cutters, FYI:
| CNC System | Overview | Features |
| Siemens SINUMERIK | Renowned for its versatility and precision. Widely used in high-performance laser cutting applications. | - Advanced automation - Intuitive user interface - High-speed processing - Extensive diagnostic tools |
| Fanuc | Leading manufacturer known for reliability and extensive functionality. | - Robust performance - User-friendly operation - High-speed and precision control - Extensive programming capabilities |
| Beckhoff | Offers open automation systems based on PC Control technology. | - Real-time control - High precision - Modular design - Seamless integration with various automation solutions |
| Bosch Rexroth | Combines high precision with ease of use, suitable for complex laser cutting tasks. | - Scalable control - High-speed processing - Advanced safety features - Excellent support for multi-axis operations |
| Mitsubishi CNC | Known for high precision and reliability. Commonly used in various laser cutting applications. | - Fast processing speed - Intuitive operation - Advanced machining capabilities - Robust hardware |
| NUM CNC | Designed for high-performance laser cutting, offering precision and adaptability for various applications. | - High-speed computation - Customizable interfaces - Multi-axis control - Efficient error handling |
| Fagor | Provides CNC systems known for their user-friendliness and robust performance in laser cutting. | - Real-time processing - High precision - Extensive customization options - Comprehensive diagnostics |
| Lantek | Offers software solutions that integrate with CNC systems to enhance laser cutting efficiency and precision. | - Advanced nesting algorithms - Real-time data processing - Intuitive interface - Support for various file formats |
| CYPCUT | Specifically designed for laser cutting machines, offering powerful and user-friendly control systems. | - Easy setup - Comprehensive cutting libraries - High-speed processing - Integrated CAD/CAM functionalities |
| NCStudio | Provides CNC systems well-suited for laser cutting, known for affordability and ease of use. | - User-friendly interface - Good compatibility with various machines - Basic and advanced cutting features - Reliable performance |
4. Motor
The motor of the laser cutting machine is the core part of the motion system. The performance of the motor directly affects the processing effect and production efficiency of the product. At present, the commonly used motors include stepper motors and servo motors. According to the type of industry and product type to be processed, a suitable motor is configured.
● Stepper motor:
Fast start-up speed and sensitive response, suitable for engraving and cutting processing with low requirements. There are many brands of stepper motors with different performances.
● Servo motor:
Fast speed, smooth movement, high load, stable performance; smooth cutting edge of processed products, fast cutting speed; high price, suitable for industries and products with high processing requirements.
5. Machine Tool
Fiber laser cutting machines have high requirements for the stability of the machine tool. High-precision, high-stability machine tools help improve the accuracy of laser cutting. At present, the mainstream machine tools on the market include gantry type, cantilever type, beam type, etc. Different machine tools have different functions. For example, beam machine tools are mainly used for material cutting in large manufacturing companies, and can also be used for model cutting in specific fields, such as 3D fiber laser cutting, which is mainly used in the automotive industry.
6. Laser Lens
Many optical devices have laser lenses. Different lenses have different functions, including full mirror, half mirror, focusing lens, etc. The quality of the lens directly affects the output power of the laser and the performance of the whole machine.
Understanding Laser Source: Types & Principle
As we mentioned before laser is the most important part in laser and different laser brands and types influence machine price significantly. If you know enough about lasers, then you have mastered the essence of laser cutting machines.
Overview of Laser Technologies
Fiber lasers are just one type of laser technology available today, alongside CO2, UV, and other laser systems. Each type of laser operates based on principles that influence:
- Material compatibility
- Application possibilities
- Operating expenses
- Maintenance requirements
Despite the differences in specific principles, all laser systems generate beams through a similar general process.
Core Components of Laser Systems
Every laser system features a "gain medium" (also known as a "laser medium" or "active medium"), which amplifies light. The gain medium can be solid, gas, or liquid, and its material affects the beam's properties. Based on the type of gain medium used, laser systems can be categorized into three types:
- Solid-State Lasers
- Gas Lasers
- Liquid Lasers
Process of Beam Generation and Formation
To create a laser beam, systems use "pump sources" (external power supplies) to energize the gain medium through a process known as "pumping." Various pump sources can be used, including flashlamps, electrical currents, and radio frequencies. Pumping excites the gain medium, causing it to release photons.
At a basic level, laser systems collect these released photons and use mirrors to amplify the energy and form a beam. Once the beam reaches sufficient strength, the system directs it toward the substrate to perform the intended application.
Operating Principles and Compatible Materials
Fiber lasers are solid-state systems that use fiber optic cables as gain mediums. These cables are lined or “doped” with rare earth ions that are ideal for receiving, storing, and emitting large amounts of energy. Put simply, fiber laser systems mark, engrave, and cut materials by:
- Using a laser diode, arc lamp, or similar light source to inject energy into the optic fiber, causing the rare earth ions to emit photons.
- Allowing the released photons to bounce within the fiber to increase energy.
- Funneling the photons toward a mirrored optical cavity where the photons are focused into a beam.
- Emitting the beam towards the substrate to complete the intended application.
These operating principles enable fiber lasers to mark, engrave, and cut a wide variety of materials with reliable speed and accuracy. Other popular laser systems, such as CO2 and UV laser models, can complete similar applications, but not always on the same materials.
Fiber, CO2, and UV laser systems all produce beams at different wavelengths, which significantly influence which materials they are compatible with. See the chart below for a general overview of which materials these systems are compatible with.
| Material Category | Material | Fiber Laser | CO2 Laser | UV Laser |
| Wood, Paper, and Board | Wood | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ |
| Thermal Label | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | |
| Paper | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | |
| Board | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | |
| Metallized Board | ✔ | ✔ | ✖ | |
| Glass | Glass | ✖ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Glass Fiber | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Ceramic | Ceramic | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Plastics | Polypropylene (PP) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| ABS | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | |
| Polyacetal (POM: polyoxymethylene) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Polyamide (PA) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | ✖ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Metals | Steel | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Galvanized Steel | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Aluminum | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Titanium | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Copper | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ | |
| Brass | ✔ | ✖ | ✔ |
As displayed in the chart above, fiber laser systems offer excellent compatibility with numerous materials, especially metals and plastics.
Fiber laser systems offer versatility for cutting, marking, or engraving various materials, but not all systems are capable of performing all these tasks. Cutting, in particular, is the most demanding application, and success depends on specific factors, primarily:
System Power: Fiber laser system power, typically measured in watts (W), is crucial for cutting various materials effectively. Here's a breakdown of power requirements for different materials:
- A 10W system is generally insufficient for cutting tasks.
- A 40W system can manage cutting thin plastic sheets.
- For thick plastic, a 200-500W system is reliable.
- To cut through thin sheet metal, a 500W system is needed.
Material Thickness: The thickness of the material being cut also plays a significant role. Thicker substrates require more power for cutting. For example:
- Thin plastic sheets may be cut with a 100W system.
- However, for metals, especially thicker ones like those used in pipe manufacturing and construction, a system with at least 1,000W is necessary for reliable cutting.

Given the substantial power requirements for cutting materials, many fiber laser systems available on the market are primarily designed for marking and engraving applications. These applications typically require lower power levels compared to cutting tasks.
By considering factors like system power and material thickness, companies can choose a fiber laser system that matches their operational needs, whether it's for cutting, marking, or engraving tasks.
Fiber Laser Buying Guide: Key Specs and Considerations
In the current landscape of fiber laser options, it's essential to grasp several key considerations to make an informed decision about which system best suits your needs. These factors include:
- Materials Compatibility: Understanding the materials you intend to work with is crucial. Whether it's steel, aluminum, rigid PVC plastic, flexible PET film, or any other material, different fiber laser systems may have varying capabilities and efficiencies with each substrate.
- Applications Requirements: Define the specific applications you need to accomplish with the fiber laser system. Are you primarily focused on cutting steel, engraving QR codes into aluminum, marking plastic with alphanumeric messages, or a combination of these tasks? Different applications may demand specific features or power levels from the laser system.
- Production Volume: Consider the volume of products or materials you need to process daily. The throughput capability of a fiber laser system can vary significantly, so it's essential to align the system's capabilities with your production requirements.
- Budgetary Constraints: Assess your budget for both the initial investment and ongoing operational costs associated with the fiber laser system. This includes not only the purchase price but also factors such as maintenance, consumables, and energy consumption over time.
While consulting an expert, like a member of Krrass machinery sales team, is advisable for tailored guidance, you can also gain a general understanding of a system's capabilities by examining key specifications. These might include laser power, maximum cutting or marking depth, supported materials, processing speed, and additional features like autofocus or rotary attachments. Evaluating these specifications against your specific requirements can help you narrow down your options effectively.
Tips for Selecting a Fiber Laser Source Manufacture
When evaluating top fiber laser source manufacturers, we prioritize several key criteria to ensure quality, reliability, and performance. Here are some essential factors to consider:
Reputation and Experience: Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation and extensive experience in the fiber laser industry. Established companies often have a track record of delivering reliable and high-quality products backed by years of expertise.
Product Quality and Certifications: Ensure that the laser sources meet stringent quality standards and certifications, such as ISO and CE. High-quality lasers not only perform better but also have longer lifespans, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Technological Innovation: Choose manufacturers that prioritize research and development to offer cutting-edge and innovative laser solutions. Advancements in technology can lead to improved efficiency, precision, and versatility in laser applications.
Customer Support and Service: Reliable customer support is crucial for addressing any issues that may arise during installation, operation, or maintenance of the laser source. Opt for manufacturers that provide comprehensive after-sales service, technical support, and training programs to assist customers effectively.
Here list important details about the top laser source manufacturers in the world.
| Ranking | Brand | Company | Year Established | Location | Employees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IPG | IPG Photonics | 1990 | USA | 5,000+ |
| 2 | Coherent | Coherent Inc. | 1966 | USA | 5,000+ |
| 3 | Raycus | Wuhan Raycus Fiber Laser Technologies Co., Ltd. | 2007 | China | 2,000+ |
| 4 | JPT | Shenzhen JPT Opto-electronics Co., Ltd. | 2004 | China | 1,000+ |
| 5 | MaxPhotonics | Shenzhen Maxphotonics Co., Ltd. | 2004 | China | 500+ |
Here are the introductions of each company with their main products and respective pros and cons, so you can make a better decision for your business.
IPG Photonics:
- Main Products: IPG Photonics specializes in high-power fiber lasers and amplifiers used in materials processing, telecommunications, medical, and scientific applications.
- Pros: Known for high-quality, reliable, and energy-efficient fiber laser solutions. IPG's lasers offer excellent beam quality, high cutting speeds, and long-term stability.
- Cons: Some customers may find IPG's products relatively expensive compared to other options in the market.

Coherent Inc.:
- Main Products: Coherent offers a wide range of laser-based solutions, including fiber lasers, diode lasers, solid-state lasers, and ultrafast lasers for various industrial, scientific, and medical applications.
- Pros: Diverse product portfolio catering to different laser applications across industries. Emphasizes innovation, reliability, and strong customer support.
- Cons: While Coherent offers high-quality products, their pricing may be on the higher side for some businesses.
Raycus:
- Main Products: Raycus specializes in manufacturing fiber laser sources for cutting, welding, marking, and engraving applications across various materials.
- Pros: Provides cost-effective fiber laser solutions without compromising quality and performance. Offers a wide range of power options to suit different application needs.
- Cons: Some users may experience challenges with customer support or service, especially for international customers outside of China.

JPT Opto-electronics Co., Ltd.:
- Main Products: JPT focuses on producing high-quality fiber laser sources primarily for marking and engraving applications, including galvo-based and fiber-coupled lasers.
- Pros: Recognized for compact and efficient fiber laser sources, offering high beam quality and precise marking capabilities. Provides customizable solutions to meet specific customer requirements.
- Cons: Limited product offerings compared to larger manufacturers, with a focus primarily on marking and engraving applications.

MaxPhotonics:
- Main Products: MaxPhotonics manufactures fiber laser sources for industrial cutting, welding, marking, and additive manufacturing applications.
- Pros: Emphasizes affordability and reliability in their fiber laser solutions. Offers robust and easy-to-integrate laser sources with competitive pricing.
- Cons: While offering cost-effective solutions, some users may find MaxPhotonics' products lacking in advanced features or customization options compared to higher-end manufacturers.

Tips for Choose The Best Laser Cutting Machine Manufacture
Selecting the right sheet metal laser cutting machine manufacturer is crucial to ensuring quality, reliability, and efficiency for your business operations. Here are some key tips to help you make an informed decision:
1. Reputation and Experience
2. Product Quality and Certifications
3. Technological Innovation
4. Customer Support and Service
5. Customization and Flexibility
6. Cost and Value

Here's a table that introduces the information about most fiber laser cutting machine manufactures in the world company, inluding their main products, and approximate price range.
| Ranking | Brand | Country | Founded | Main Products | Approximate Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trumpf | Germany | 1923 | Fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, laser cutting machines | $100,000 - $1,000,000+ |
| 2 | Hanslaser | China | 1996 | Fiber lasers, laser marking machines, laser welding | $50,000 - $500,000 |
| 3 | HGTECH | China | 1999 | Laser cutting machines, laser marking, laser welding | $50,000 - $600,000 |
| 4 | Bystronic | Switzerland | 1964 | Laser cutting systems, bending machines | $200,000 - $1,200,000+ |
| 5 | Krrass | China | 1995 | Tube and pipe lasers, fiber laser cutting machines | $15,000 - $100,000 |
| 6 | PrimaPower | Italy | 1977 | Laser cutting machines, punching machines | $150,000 - $900,000 |
| 7 | AMADA | Japan | 1946 | Laser cutting machines, press brakes | $150,000 - $1,000,000+ |
| 8 | Mazak | Japan | 1919 | Laser cutting machines, multi-tasking machines | $200,000 - $1,000,000+ |
Unlock Cutting-Edge Technology with KRRASS Laser Systems
KRRASS offers a top-rated fiber laser cutting machine specifically designed for metal fabrication. It is capable of cutting a variety of metals including steel, aluminum, titanium, alloys, brass, copper, and iron. Available in different laser power options (1000W, 1500W, 2000W, 3000W, 4000W, 6000W, 8000W, 12000W, and 20000W), this affordable fiber laser cutter delivers high performance at a competitive price. KRRASS provides exceptional service and support for their fiber laser cutting systems, ensuring the best experience for users.
Advantages of Krrass Fiber laser cutting machine
- High Precision and Accuracy
- Wide Range of Power Options
- Material Versatility
- Efficiency and Speed
- Low Maintenance Requirements
- Cost-Effectiveness
Smart Series Fiber Laser Cutting Machine with High Configurations
- Super heavy Steel Welding Machine Bed
- The Fifth-generation Aviation Aluminum Alloy Beam
- Intelligent Control System
- Auto focusing laser head
- Packed in a 20GP container for easy transportation





