If you are new to the world of metalworking or fabrication, investing in a plasma cutter CNC can be a game-changer. A plasma cutter CNC combines the precision of computer numerical control (CNC) with the power of plasma cutting technology to create an efficient and accurate cutting tool for a wide range of materials. From custom fabrication projects to heavy industrial applications, a plasma cutter CNC allows for high-quality cuts on metals like steel, aluminum, and copper. This guide will walk you through the basics of plasma cutter CNC machines, helping beginners understand how they work, what features to look for, and how to safely operate them.
What is a Plasma Cutter CNC?
A plasma cutting torch is a commonly used tool for cutting metals for a wide variety of purposes. A hand-held plasma torch is an excellent tool for quickly cutting through sheet metal, metal plates, straps, bolts, pipes, etc. Hand-held plasma torches also make an excellent gouging tool, for back-gouging weld joints or removing defective welds. A hand torch can be used for cutting small shapes from steel plates, but it is impossible to get good enough part accuracy or edge quality for most metal fabrication. That is why a CNC plasma is necessary.
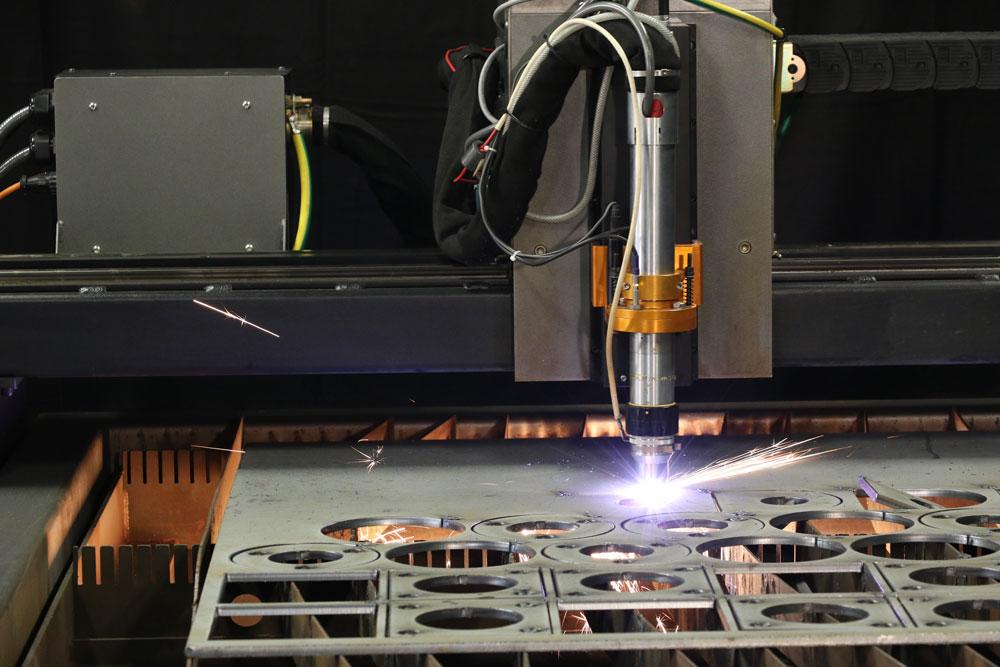
CNC Plasma Cutter Features
Your choice of CNC plasma cutter will depend on the following factors:
- Metal thickness: It’s critical to measure the thickness of the metal you intend to cut. Doing so will help you decide which plasma cutting machine to invest in. For instance, a 55mm (20-1/4”) metal sheet can be easily cut with a Powermax plasma cutter.
- Plasma cut quality: Get an idea of the machine’s potential cut quality by considering the plasma cutting system, motion control devices, type of machine, and process variables. Modern CNC plasma cutters use a tightly focused arc that provides a straight, clean, and smooth cut.
- Duty cycle: The duty cycle of any metal cutting machine will decrease as the user increases the voltage. So consider machines that offer the highest percentage number at any amperage—these are the cutters most likely to last longer.
- Plasma cutting torch length: The general rule is to choose a machine with a torch that fits the shape of your hand. However, a longer torch would be needed if you work in a large space, so you don’t have to move the plasma cutting machine around.
- Voltage: Three voltage options are available for plasma cutters: 115V, 230V, and dual voltage. 115V cutters can be plugged into a standard home power outlet, but a 230V machine is better for industrial use.
- Pilot arc: Check whether the machine you’re considering buying has a pilot arc. This is handy for cutting rusty services because it removes the need to clean and strike the metal.
- Consumption rate: Consider the consumption rate of your machine to reduce costs over time. Plasma cutters from Hypertherm cost more upfront, but their robust consumables help lower operating costs, making them an excellent choice for saving money in the long run.
Software: Top quality designs require the operator to use a combination of CAM, CNC, and CAD software. Inquire about software options with the vendor before making a buying decision.
Parts of the CNC Plasma
The CNC machine may be an actual controller designed for machine tools, with a proprietary interface panel and a specially designed control console, such as a Fanuc, Allen-Bradley, or Siemens's controller. Or it could be as simple as a Windows-based laptop computer running a special software program and communicating with the machine drives through the Ethernet port. Many entry-level machines, HVAC machines, and even some precision unitized machines use a laptop or desktop computer as the controller.
To cut parts from steel plates, the motion of the torch is controlled by the CNC. The part program, usually just a text file with “M-codes” and “G-codes”, describes the contours of the part and when to turn the torch on and off. Part programs are usually created by a piece of software called a “post-processor”, which can take a part geometry from a CAD file and translate it into M-codes and G-codes that the CNC can read.
A CNC plasma machine also requires a drive system, consisting of drive amplifiers, motors, encoders, and cables. There will be at least two motors, one for the X-axis and one for the Y-axis. There is a drive amplifier for each motor, which takes a low-power signal from the CNC and turns it into a higher-powered signal to move the motor. Each axis has a feedback mechanism, usually an encoder, which creates a digital signal indicating how far the axis has moved. Cables take the power from the amplifier to the motor and carry the position signals from the encoder back to the CNC.
The CNC reads the part program and then outputs signals to the machine’s drive system which moves the torch in the desired direction at the programmed speed. The CNC reads the encoder feedback and makes corrections to the drive signals as required to keep the torch motion on the programmed path. All the electronics in the CNC and drive system work and communicate very quickly, often measuring and updating position information every few milliseconds. This allows the machine motion to be smooth and accurate enough to produce plasma cut parts with a smooth, straight, consistent edge quality, and precise part dimensions.
Finally, a CNC plasma system will have some sort of “I/O system”, an electrical system that handles Inputs and Outputs. This is how the CNC turns on the plasma at the appropriate time, by turning on an output that closes a relay, for example. The CNC uses inputs to know when the plasma arc has started and is ready to move. Those are the most basic Inputs and Outputs required, but obviously, there can be many more.
How It Works
CNC plasma cutting machines are computer-run systems that have the ability to move a high-definition plasma torch in various directions by using the numerical coding that has been programmed into the computer. The high-definition plasma cutter itself operates by forcing a gas or compressed air through a nozzle at high speeds. An electric arc is then introduced to the gas, creating plasma which is able to cut through metal.
CNC plasma cutters are available in a range of different sizes, prices, and functionalities. These machines are highly accurate and can slice through metals at speeds of up to 500 inches per minute. While high-definition plasma cutters require a plasma gas and an assist gas to function, the type of gas will vary depending on the material being cut. Some of the gases that can be used in plasma cutting include:
- Oxygen—can be used to cut mild steel up to 1 1/4 inches thick but causes rough-looking cuts in stainless steel and aluminum.
- Argon and hydrogen mix—provides high-quality, smooth cuts in stainless steel and aluminum.
- Compressed air—works well for low current cutting applications in metals up to 1 inch thick.
- Nitrogen—can be used to cut thin stainless steel.
- Methane—can be used to cut thin stainless steel.
Plasma Cutter Temperature: How hot is a plasma cutter?
Plasma torches can reach a whopping 40,000° F. This occurs almost instantaneously as soon as the torch is turned on, so no warmup time is required. At that temperature, most materials cannot withstand it, causing a quick, accurate cut.
Advantages of Using a Plasma Cutter CNC
High Precision and Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of a plasma cutter CNC is its exceptional precision. By integrating computer numerical control (CNC) technology, the machine can execute highly detailed cuts with exact measurements. This level of precision is crucial for industries where accuracy is essential, such as automotive manufacturing and metal fabrication. The CNC system ensures consistent and repeatable results, making it ideal for complex designs or large production runs.
Speed and Efficiency in Metal Cutting
Plasma cutter CNC machines are renowned for their speed, significantly reducing the time needed for metal cutting tasks compared to manual methods. The plasma torch can cut through various thicknesses of metal swiftly and cleanly, optimizing production processes. Additionally, the automated nature of CNC programming allows for continuous operation with minimal human intervention, further boosting overall efficiency. This makes plasma cutter CNC machines a cost-effective solution for industries looking to enhance productivity.
Versatility in Handling Different Materials
Plasma cutter CNC machines are highly versatile, capable of cutting a wide range of conductive materials. From mild steel and stainless steel to aluminum and copper, plasma cutters can handle varying thicknesses with ease. This versatility makes them suitable for a broad spectrum of industries, including construction, aerospace, and artistic metalwork. Whether you're working on heavy-duty industrial projects or custom metal designs, a plasma cutter CNC offers the flexibility needed to handle different materials and job requirements.
What Gases Are Used for Plasma Cutting
This is one of the more interesting aspects of the plasma cutting process as there are different gasses for different metals and different qualities of cuts.
For Mild Steel: For a quicker, less detailed cut, you would use oxygen on mild steel up to 1 ¼ inch thick. However, if you used oxygen on stainless or aluminum, it would produce a much rougher looking cut.
For Stainless Steel or Aluminum: For smooth, high-quality cuts on stainless steel and aluminum, you utilize a mixture of argon and hydrogen.
How Thick Can a Plasma Cutter Cut
Not all CNC plasma cutters are built the same, however, some can cut through almost 6 inches of steel!
What Designs Can the CNC Plasma Cutter Create?
The possibilities are practically limitless in terms of designs. However, a rule of thumb to follow in the world of CNC designs is that the more detail you want in a design, the larger the end product must be. This is to prevent cuts from going into each other and ruining the integrity of the piece, as the torch runs so hot that it can bleed into other existing cuts.
Differences Between CNC plasma cutters and Other CNC Cutters
The main differences between CNC plasma cutters and other CNC cutters, such as laser cutters and waterjet cutters, lie in their cutting methods, materials they are best suited for, precision, cost, and applications. Below is a breakdown of these key differences:
1. Cutting Method
- CNC Plasma Cutter: Uses a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials, typically metals like steel, aluminum, or copper. Plasma is created by heating a gas to extremely high temperatures, ionizing it, and directing it through a nozzle to melt and blow away material.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Utilizes a focused laser beam to vaporize, melt, or burn materials. Laser cutters can work on a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and textiles.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: Uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive substance, to cut through almost any material, including metal, stone, glass, composites, and ceramics. It cuts without heat, making it ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures.
2. Materials
- CNC Plasma Cutter: Primarily for cutting metals (mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum). It’s not suitable for cutting non-conductive materials like wood or plastic.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Versatile and capable of cutting both metallic and non-metallic materials, such as steel, aluminum, wood, plastics, and even fabrics.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: Can cut virtually any material, from metals to composites, rubber, glass, and stone. It is one of the most versatile cutting machines in terms of material compatibility.
3. Precision
- CNC Plasma Cutter: Offers good precision for metal cutting but less precise compared to laser or waterjet cutters. Typical tolerances range from ±0.01" to ±0.03".
- CNC Laser Cutter: Extremely high precision, with tolerances typically around ±0.001" to ±0.005". It’s ideal for fine details and intricate designs.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: Offers very high precision, similar to laser cutters, with tolerances of ±0.003" to ±0.005". Suitable for detailed work without causing heat damage.
4. Cutting Speed
- CNC Plasma Cutter: High cutting speed, especially for thicker metals (up to 2 inches or more). Plasma cutting is faster than both laser and waterjet when working on thick metals.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Speed varies depending on material and thickness, but laser cutting is generally faster than waterjet cutting for thinner materials, especially in non-metal applications.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: Slower cutting speeds, especially for thicker or harder materials. It is slower compared to plasma and laser cutting due to the abrasive process and pressure limitations.
5. Cost
- CNC Plasma Cutter: More affordable than laser and waterjet cutters, especially for cutting thick metals. Initial costs and operating costs are lower, making plasma cutters a cost-effective choice for metalworking.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Higher initial costs and operating expenses due to the need for specialized equipment (laser sources) and maintenance. However, the precision and versatility justify the price for many industries.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: The most expensive option due to the high cost of the waterjet pump and the need for abrasives. Operating costs are also higher because of water consumption and abrasive materials.
6. Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
- CNC Plasma Cutter: Generates heat, which can create a heat-affected zone (HAZ) on the cut edges. This may require additional post-processing to smooth or clean the edges.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Also generates heat, though the heat-affected zone is typically smaller than that of plasma cutters. However, on thick metals, there can still be some warping or distortion.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: No heat is involved, making it ideal for materials sensitive to heat (e.g., plastics, rubber, or metals that may warp due to heat). No HAZ is produced, resulting in clean cuts without thermal distortion.
7. Applications
- CNC Plasma Cutter: Best suited for cutting thick metal plates, steel structures, and metal fabrication industries. Common in automotive repair, industrial construction, and shipbuilding.
- CNC Laser Cutter: Used in industries requiring high precision and versatility, such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, signage, and jewelry making. It can handle both metals and non-metals.
- CNC Waterjet Cutter: Ideal for cutting a wide variety of materials, from metals to glass and stone. Commonly used in aerospace, architectural, and engineering industries where precision and versatility are key.
Summary
- CNC Plasma Cutters excel at cutting thick metals quickly and affordably but lack the precision and versatility of laser and waterjet cutters.
- CNC Laser Cutters offer superior precision and are highly versatile, cutting both metals and non-metals, but they come at a higher cost.
- CNC Waterjet Cutters provide the most versatility in terms of materials, produce no heat-affected zones, and are very precise, but they are slower and more expensive to operate.
Your choice of CNC cutter depends on the materials, precision, and budget required for your specific application.
Plasma Cutter CNC Applications
CNC plasma cutters are used in a wide range of residential and industrial workshops for different cutting applications. Typical applications include:
- Straight cutting
- Hole cutting
- Bevel cutting
- Fine feature cutting
- Extended reach cutting
- Chain cutting
- Bridge cutting
- Multi-head cutting
- Marking
- Gouging
Modern plasma cutters also help reduce the amount of debris created in the environment. Some models combat noise, while others enable arc cutting under water. HTPAC (high tolerance plasma arc cutting) is an important evolution of arc technology. The process is deemed a low-cost alternative to laser cutting and offers great precision on material 12mm thick and below.
CNC Plasma Cutters vs. Oxy-Fuel Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutters face some competition from oxy-fuel cutting machines. These machines rely on a fuel/oxygen gas flame to preheat metal to its temperature. Those working in the metalworking industry often prefer plasma cutters over oxy-fuel because the plasma system does not require preheating. Additionally, the quality and speed of plasma cutting are far better than flame oxy-fuel cutting.
Other benefits of plasma cutters include:
- Smaller cutting kerf than flame cutting
- Most efficient way to cut medium thickness aluminum and stainless steel
- Can cut in water, producing smaller HAZ
- Excellent quality cuts for thickness up to 50 mm
- Relatively cheap with plates starting at around 15 mm
- Eliminates plate warping and diminishes dross
What Is the Thickest a Plasma Cutter Can Cut?
Plasma cutters are used to perform cutting and gouging operations, with the average hand-held system capable of cutting a maximum metal thickness of about 1 inch. Plasma typically requires a source for compressed air and a substantial amount of electrical power.
CNC Plasma Cutter Brands
There are several well-known brands that manufacture high-quality CNC plasma cutters. These brands are recognized for their performance, reliability, and advanced technology. Here’s a list of top CNC plasma cutter brands:
1. Hypertherm
- Overview: Hypertherm is a leading global manufacturer of plasma cutting systems and is widely regarded for its innovation and high-quality machines. Known for producing precise and efficient plasma cutters, Hypertherm offers a range of products for both industrial and hobbyist use.
- Popular Models: Powermax Series (Powermax45, Powermax65, Powermax85), XPR300
- Key Features: High-precision cutting, user-friendly controls, and long consumable life.
2. Lincoln Electric
- Overview: A global leader in welding and cutting equipment, Lincoln Electric also produces high-performance CNC plasma cutters. They are known for durable construction and efficient performance in demanding industrial environments.
- Popular Models: FlexCut 80, FlexCut 125
- Key Features: High cutting speed, excellent accuracy, and advanced automation options.
3. Thermal Dynamics (ESAB)
- Overview: Thermal Dynamics, part of the ESAB Group, is another leading plasma cutter manufacturer known for its innovative products and technology in the cutting industry. Their plasma cutting systems are designed for both small and large-scale applications.
- Popular Models: Cutmaster Series (Cutmaster 60i, Cutmaster 40), A-Series Automation
- Key Features: Lightweight, portable, high power output, and reliable performance.
4. Miller Electric
- Overview: Miller Electric is one of the most trusted names in the welding and cutting industry. Their CNC plasma cutters are well-known for ease of use and robust design. Miller caters to both professional and entry-level users.
- Popular Models: Spectrum Series (Spectrum 375, Spectrum 625 X-Treme)
- Key Features: Portable, reliable, smooth cuts, and intuitive operation.
5. Hobart
- Overview: Hobart specializes in creating reliable plasma cutters for both industrial and light-duty applications. They offer cost-effective machines that are user-friendly and deliver consistent performance.
- Popular Models: AirForce 12ci, AirForce 27i
- Key Features: Lightweight, compact, and affordable machines with built-in air compressors for added convenience.
Conclusion
A plasma cutter CNC is a powerful and versatile tool, offering precision, efficiency, and flexibility for a variety of metal cutting applications. Whether you're just starting in metalworking or looking to upgrade your fabrication process, understanding the basics of how a plasma cutter CNC operates, its key components, and its advantages is essential. With the right machine, beginners can quickly master cutting techniques and take on projects ranging from small custom designs to large-scale industrial work. By following this guide, you'll be well-equipped to choose the best plasma cutter CNC for your needs and start creating with confidence.



