Are you in search of a hydraulic press brake machine? Do you need clarification about the various types of hydraulic press brakes and deciding which one to choose? Well, worry no more!
This article will discuss the differences between NC and CNC hydraulic press brake machines. These machines are crucial in metal fabrication and bend cold metal sheets into geometric shapes.
With advancements in technology, the coordinate axes of hydraulic press brake machines have evolved from single-axis to as many as twelve axes. But what sets apart NC and CNC hydraulic press brake machines? Which device is more suitable for your needs?
We will explore each type's structural principles, workpiece precision, and other critical features to help you make an informed decision.
Therefore, whether you are an experienced metalworker or a newcomer to the industry, this article suits you.
Continue reading to learn more about NC and CNC hydraulic press brake machines and find the perfect device to enhance your metal fabrication capabilities.
What is a Hydraulic Press Brake Machine?
A hydraulic press brake machine is used in the metalworking and manufacturing processes for bending and forming metal sheets. It utilizes hydraulic force to apply pressure on the metal workpiece, bending it into the desired shape. The machine consists of a hydraulic system, a bending tool (also known as a punch), and a die.
The hydraulic system provides the necessary power to control the movement of the punch and apply pressure to the workpiece. The bending tool is mounted on the machine's stroke or upper beam to exert force on the workpiece. The die is located on the bed or lower shaft, providing a surface on which the workpiece relies during bending.
The hydraulic press brake operator sets the desired bending parameters, such as angle, length, and depth, and adjusts the machine accordingly. The hydraulic system is activated once the workpiece is correctly positioned between the punch and die, applying pressure to bend the metal.
Hydraulic press brake machines offer precise control over the bending process and can handle metal sheets of various thicknesses and materials. They are widely used in automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing industries to produce multiple metal components and structures.
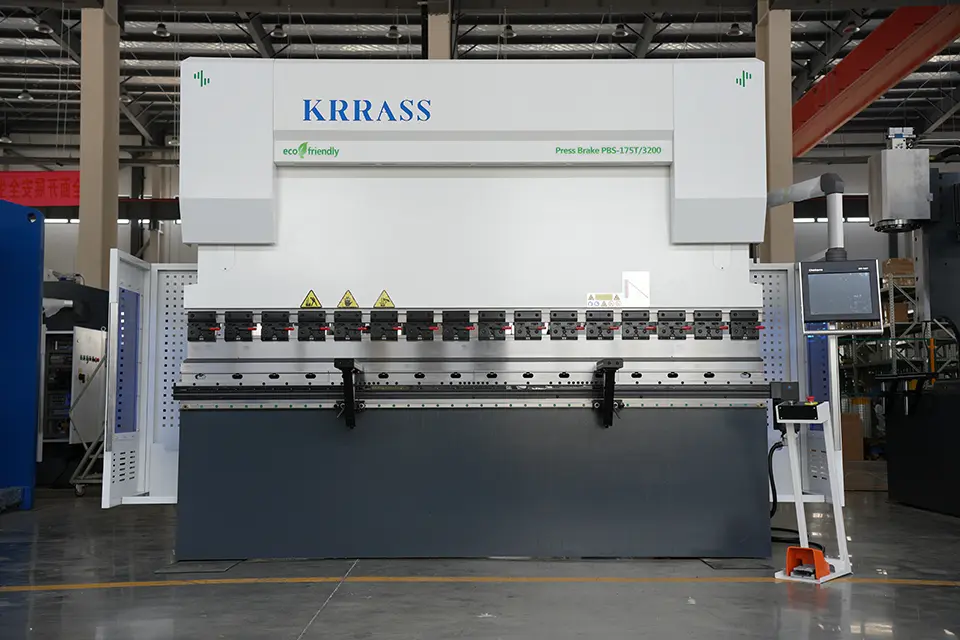

Typically, press brake machines employ dedicated numerical control systems.
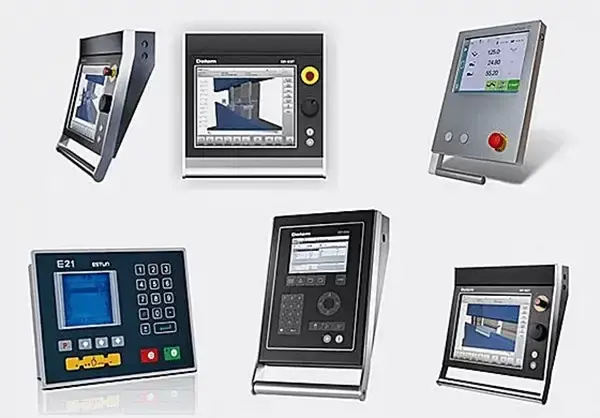

The coordinate axes of press brake machines have evolved from single-axis to as many as twelve axes, classified based on their functions, as follows:
- X-axis: Controls the front-to-back movement of the back gauge
- Y-axis: Controls the stroke of the hydraulic cylinder
- Z-axis: Controls the left-to-right direction of the back gauge
- R-axis: Controls the up-and-down movement of the back gauge
- V-axis: Mechanical crowning axis
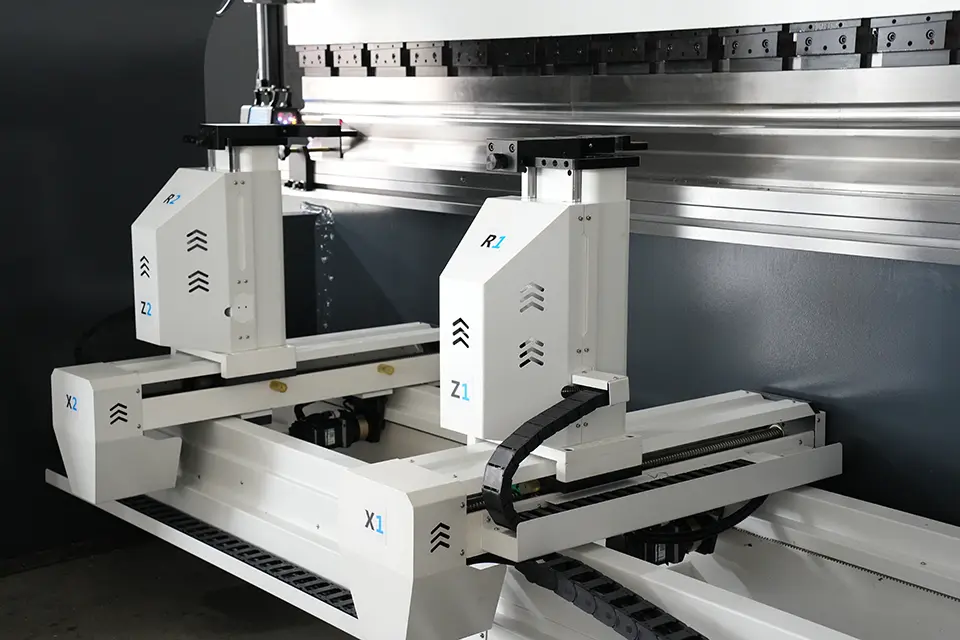

With the numerical control system, the hydraulic press brake machine can achieve automatic control over various aspects of the punching operation. It can precisely regulate the depth of punch operation, fine-tune the left-to-right tilt of the punch, adjust the front-to-back and left-to-right position of the back gauge, control the pressure tonnage, and even customize the approach speed of the punch. These features empower the machine to operate with high precision and flexibility, enhancing the overall performance of the bending process.
Hydraulic press brake machines allow for easy execution of actions such as the downward motion of the punch, micro-jogging, continuous pressing, return, and mid-stop. They can also perform multiple bends simultaneously, whether at the same or different angles.
Components of a Hydraulic Press Brake Machine
Punch
The punch component is commonly driven by hydraulic transmission in hydraulic press brake machines. It comprises a punch, oil cylinder, and mechanical fine-tuning structure. The NC system controls and adjusts the values of the mechanical fine-tuning, ensuring precise customization of the machine's settings.
Synchronization System
The synchronization system is mainly designed with mechanical components, offering a simple structure and stable, reliable performance. Its key components include a torsion shaft, swing arm, and coupling.
Worktable Part
A control panel controls the worktable part, and the numerical control system adjusts the movement distance. Limit switches are also installed for front and rear positions.
Backgauge Structure
A motor drives the back gauge structure, and the numerical control system controls its movement.
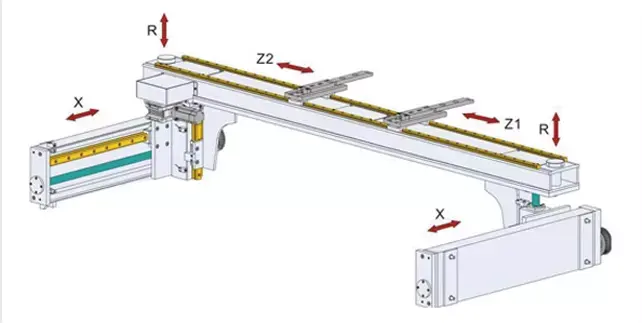
Types of Press Brake Machines
Press brake machines primarily refer to machines used for bending and forming various metal sheets. These devices are commonly used for sheet metal bending and are considered large-scale machines. The selection of a press brake should be based on factors such as intended use, working environment, required bending capacity, sheet metal thickness, and other relevant conditions. Understanding how to choose the appropriate type is essential knowledge.
Press brake machines can be classified according to their working characteristics and modes. Here is a comprehensive overview of the classification of press brake machines:
1. Manual Press Brake Machines
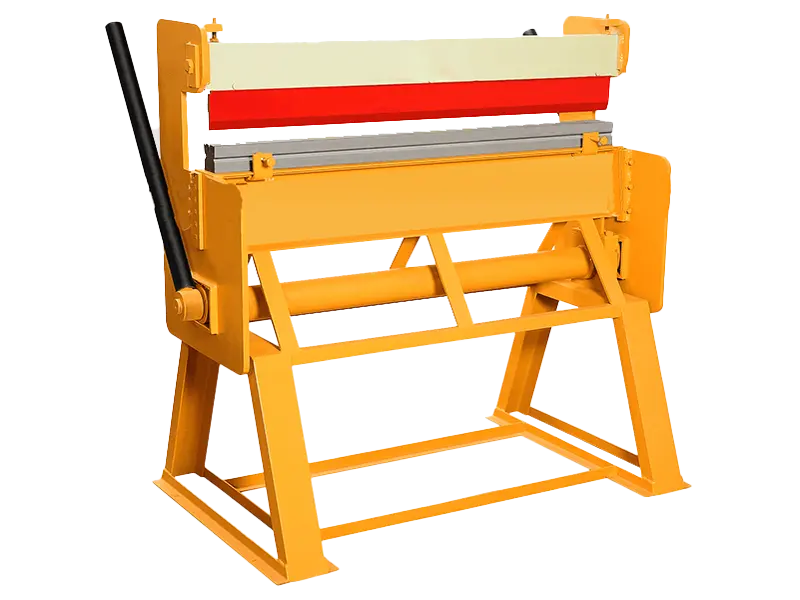

There are two types of manual press brake machines: mechanical manual press brakes and electric manual press brakes. These bending machines are widely recognized and sought after domestically and internationally due to their compact size, high efficiency, low energy consumption, large and fast production capacity, broad applicability, and ease of transportation. Manual press brake machines feature relatively simple structures and require manual operation. They are well-suited for processing and manufacturing small-sized workpieces.
2. Hydraulic Press Brake Machines
Hydraulic press brake machines can be classified based on their synchronization methods, such as torsion bar synchronized press brakes, mechanical-hydraulic synchronized press brakes, and electro-hydraulic synchronized press brakes. Based on their motion modes, hydraulic press brake machines can be divided into up-acting and down-acting press brakes. Hydraulic press brake machines find extensive applications in industries such as automotive, doors and windows, steel structures, and metal sheet V-grooving.
Here are the main features and characteristics of hydraulic press brake machines:
- They adopt fully welded steel structures, achieving high strength and rigidity through stress elimination by vibration.
- They utilize hydraulic transmission, ensuring stability and reliability.
- They employ mechanical back gauges and torsion bar synchronization, offering high precision.
- The back gauge distance and upper slide stroke can be electrically adjusted and fine-tuned manually, equipped with digital displays.
3. NC/CNC Press Brake Machines
At the heart of NC Press Brake or CNC press brake machines lies the bending tool designed for sheet metal. This tool comprises a support, worktable, and clamping plate. By energizing a coil, the clamping plate applies force to secure the sheet metal between itself and the base. Based on the electromagnetic force, this clamping method allows customization of the clamping plate to accommodate specific workpiece requirements. Consequently, the operation becomes straightforward, and the machine can effectively process workpieces with sidewalls.
NC Press Brake or CNC press brake machines are modern large-scale machines widely favored for their high precision. They provide:
- Flexible operating modes.
- We allow connection with two bending machines for lengthy sheet metal processing or operating as a single machine.
- It is improving efficiency.
- It reduces energy consumption.
- We are facilitating operation through automatic compensation adjustments by the CNC system.
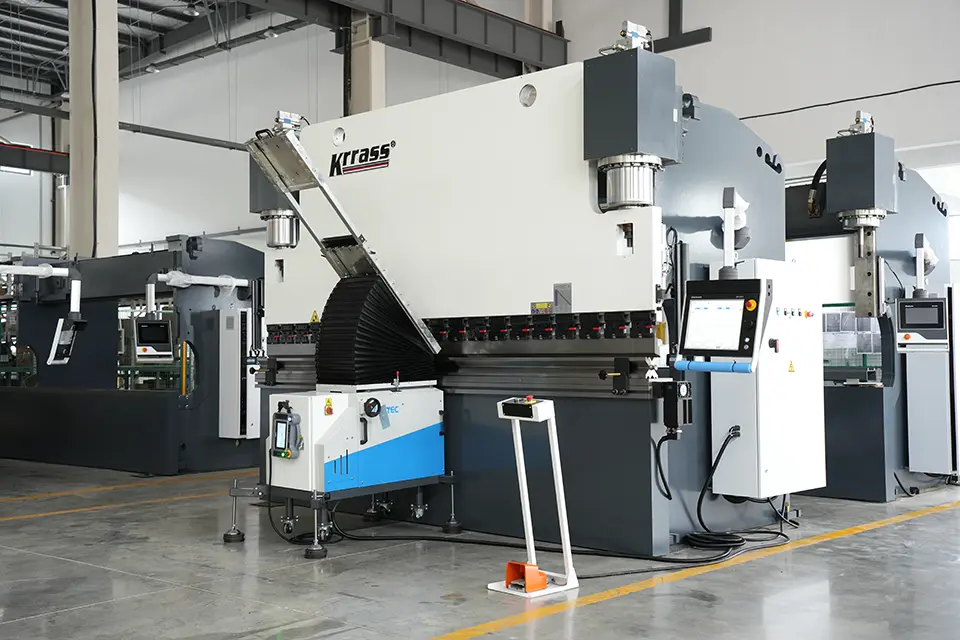

NC/CNC press brake machines come in various models, including the PBK, PBS, and WC67K series produced by KRRASS. Different types of press brake machines have unique performance and application areas. Therefore, selecting the appropriate machinery based on usage and operating environment is crucial for achieving optimal performance.
Differences Between NC and CNC Press Brake Machines
What are the differences between torsion bar synchronized press brakes and electro-hydraulic synchronized press brakes (referring to NC and CNC press brake machines)? Numerous bending devices are available in the market with different configurations and systems. Torsion bars and electro-hydraulic press brakes are often compared due to their similar functionalities, but they have different advantages in terms of components, systems, and prices. With numerous options, selecting a bending machine that delivers superior performance, cost-effectiveness, and user-friendliness can be challenging. To address this, we will compare NC and CNC press brake machines from various angles in the following sections. By doing so, we provide you with valuable insights to make an informed decision.
Different Structural Principles
These two models have different design principles, leading to different structures to ensure the synchronization of the bending punch on both sides.
NC press brake machines use torsion bars to connect the left and right swing arms, forming a torsion bar-forced synchronization mechanism that drives the up-and-down movement of the cylinders on both sides. Therefore, NC press brake machines operate based on a mechanical forced synchronization mode and lack the ability to monitor or adjust the parallelism of the punch automatically.
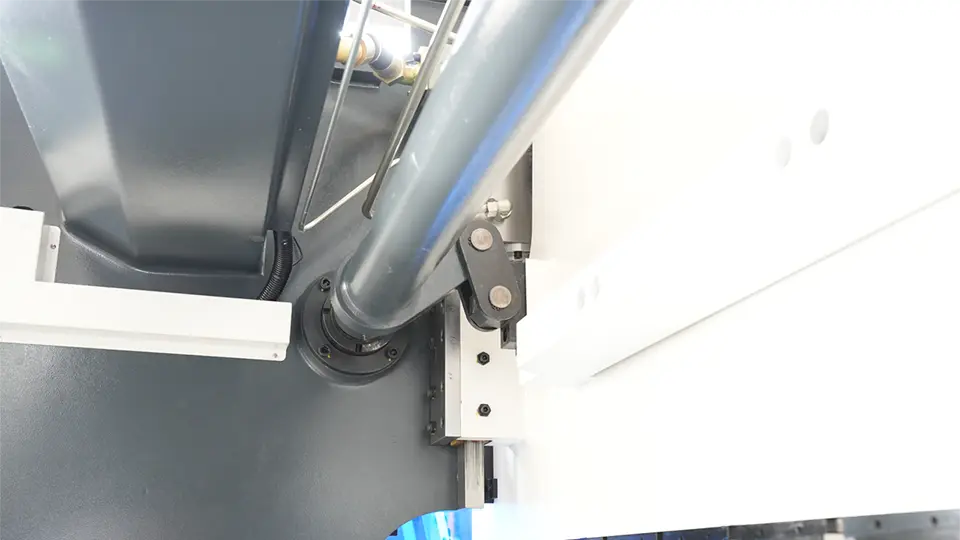

On the other hand, CNC press brake machines are equipped with linear encoders installed on the punch or the bed. The CNC system continuously analyzes the synchronization of both sides of the punch based on feedback from the linear encoders.
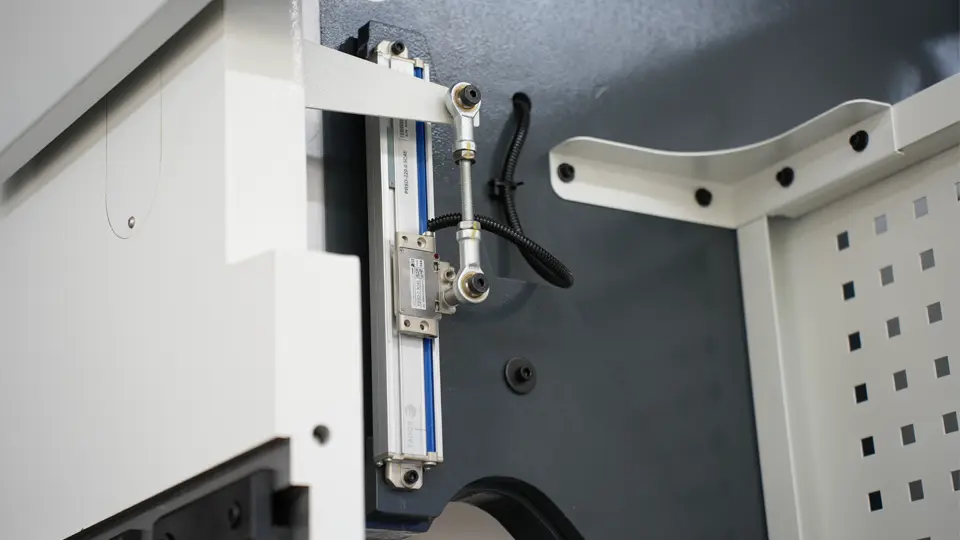
When errors occur, the CNC system adjusts the synchronization by proportionally controlling the electro-hydraulic servo valves, ensuring the parallelism of the punch.
Workpiece Precision
The parallelism of the punch determines the angle of the workpiece. NC press brake machines maintain synchronization of the punch through mechanical means, lacking real-time error feedback and automatic correction capabilities, resulting in poor machining precision. Additionally, due to the torsion bar forced synchronization mechanism driving the up and down movement of the cylinders on both sides, the load-bearing capacity of NC press brake machines is limited, and the torsion bar may deform over time under partial load.
On the other hand, CNC press brake machines control the synchronization of the punch using proportional electro-hydraulic valves and obtain real-time error feedback from linear encoders. When errors occur, the system adjusts the punch to maintain synchronization and improve machining precision.
Operating Speed
Three factors determine the speed of a press brake machine during operation:
- Punch speed
- Backgauge speed
- Bending steps
NC press brake machines typically use 6:1 or 8:1 cylinders, resulting in slower speeds. In contrast, CNC press brake machines use 13:1 or 15:1 cylinders, providing faster speeds. As a result, CNC press brake machines exhibit significantly higher speeds in a rapid descent and return compared to NC press brake machines.
While NC press brake machines have the functions of both rapid and slow descent of the punch, the speeds of rapid descent and return are only 80mm/s, and the speed transition is not smooth. The running speed of the back gauge is only 100mm/s.
In comparison, CNC press brake machines feature rapid and slow descent of the punch, with rapid descent and return speeds of up to 200mm/s and smooth speed transitions, greatly improving production efficiency. The running speed of the back gauge is 400mm/s.
Mechanical Strength
Due to design limitations, NC press brake machines cannot perform bending under eccentric loads. Long-term bending under eccentric loads can cause deformation of the torsion bar. However, CNC press brake machines do not have this issue. The Y1 and Y2 axes on the left and right sides can operate independently, allowing bending under partial loads.
Practical Operation
Most NC press brake machines lack a CNC system and V-axis compensation.
Therefore, when processing based on drawings, it relies on experienced workers for trial bending. If the results do not meet the standards, additional trials are required, leading to wastage, and there is a limited number of highly skilled operators available at high wages.
Although a manual crowning system can be added, CNC press brake machines, controlled by a dedicated CNC system, have V-axis compensation, making the operation easier and requiring less operator experience.
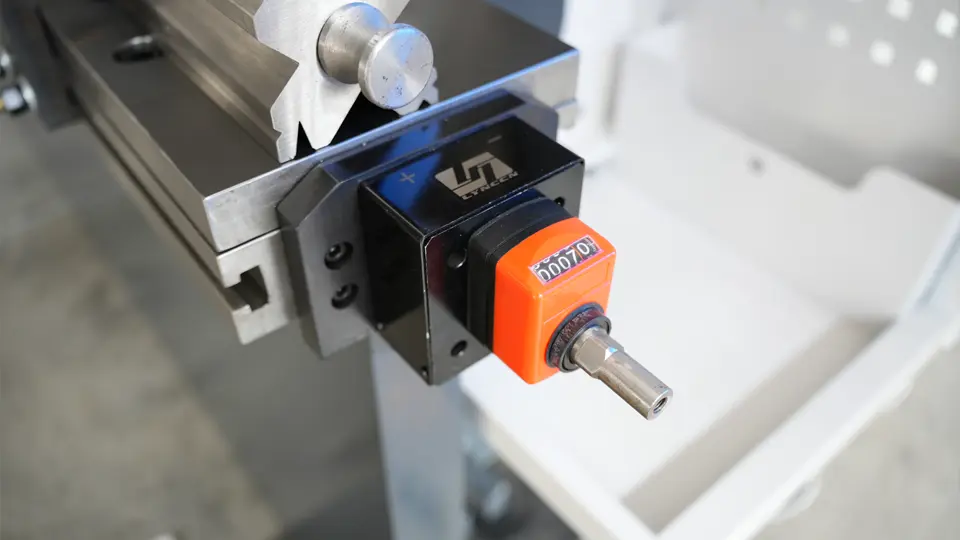

CNC press brake machines can simulate bending without the need for trial bending; adjustments are made based on drawings, inputting steps, and dimensions, and then directly proceeding with the bending process.
Number of CNC Axes
The more control axes an NC press brake machine has, the less pronounced its effects. Typically, it controls only the X and Y axes.
In contrast, CNC press brake machines have no limitations on the number of controlled axes. They can be 3+1 axes or more, equipped with automatic program design capabilities, meeting high requirements such as 4+1 axes, 5+1 axes, 6+1 axes, 7+1 axes, 8+1 axes, and more.
Good Optional Components
NC press brake machines can be improved by adding better components, such as quick-change tooling, manual crowning, up and down sheet supports, ball screws, linear guide back gauges, oil coolers, and laser guards.
In comparison, CNC press brake machines have these essential components and can be equipped with various high-quality accessories. For example, standard tooling can be replaced with quick-change toolings like Tyokko or Amada types. The up and down sheet support can be operated manually or electrically by an AC motor on rails. The laser guard can be replaced with a more sensitive laser protection system. CNC press brake machines can also be equipped with servo pump control systems for energy-saving, low-noise operation, faster punching speeds, and lower fuel consumption, as well as a manipulator's arm to improve production efficiency, hydraulic clamping systems, follow-up supports, and laser angle detectors.
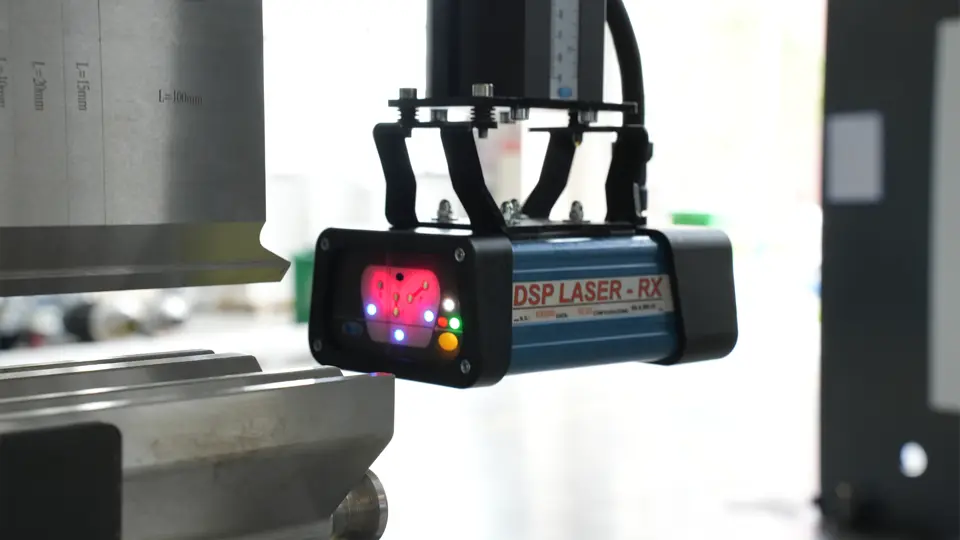

The main difference between CNC and NC press brake machines lies in the presence of feedback control loops and CNC crowning systems.
The difference between the two should be clear. NC press brake machines adjust the cylinder stroke mechanically, while CNC press brake machines control the stroke hydraulically. A balancing shaft controls NC press brake machines, while CNC press brake machines synchronize both sides using servo-proportional valves.
CNC press brake machines combine the advantages of electrical and hydraulic systems, offering high control precision, rapid response speed, large output power, flexible signal processing capabilities, and the ability to monitor various parameters easily. The efficiency of a CNC press brake machine can be equivalent to two to three NC press brake machines.
Advantages of CNC Press Brake Machines
- Punch Synchronization: CNC systems offer stable and flexible synchronization of the punch, with the ability to detect and correct punch tilting.
- Bending Angle (Depth): The CNC system can automatically calculate the bending depth based on selected die angles, opening, R dimensions, and sheet thickness.
- Bending Depth Feedback: Reliable imported linear encoders directly measure the position on both sides of the punch, including mechanisms to compensate for throat deformation, ensuring consistent angles.
- Worktable Deflection Compensation: The CNC system can calculate the pressure needed to compensate for worktable deflection during the bending process, ensuring uniform angles throughout the length and improving the straightness of the workpiece.
- Angle Correction: When there is a deviation between programmed and actual formed angles, users can input the error value, and the system will automatically compensate and correct it.
- Stop Positions: The system can calculate the position of each stop axis based on the bending height, allowing for quick and convenient step changes and corrections.
- Programming Modes: The system offers graphical and data programming options, enabling fast and convenient program modifications and edits.
- Unfolding Length: The CNC system can calculate the unfolding length based on graphical programming and external or internal dimensions.
- Interference Calculation: The CNC system can automatically determine the optimal bending process based on programming graphics, die shapes, and machine configurations, alerting the user in case of bending interference. Users can also manually modify the bending process.
These advantages make CNC press brake machines highly efficient, precise, and user-friendly, providing extensive capabilities for various bending operations.
How to Choose a Hydraulic Press Brake?
In summary, the choice of a hydraulic press brake depends on specific processing requirements.
CNC press brake machines offer high precision, real-time error feedback, and strong resistance to eccentric loads. In contrast, NC press brake machines have lower precision, lack error feedback capabilities, and have poorer resistance to punch deflection loads. Additionally, CNC press brake machines are more complex and expensive than NC press brake machines.
When making a decision, consider the following factors:
- Precision requirements of the workpiece: CNC press brake machines offer higher precision than NC press brake machines.
- Daily working hours: CNC press brake machines are more efficient and can reduce work time and labor costs.
- Experience of machine operators: NC press brake machines require experienced operators, while CNC press brake machines are simpler to operate through system controls.
- Failure rate: Frequent breakdowns can lower efficiency and prolong construction time. CNC press brake machines have a much lower failure rate.
- Available funds: CNC press brake machines are the better choice if the budget allows it. However, if the budget is limited, NC press brake machines may be a more feasible option.
Considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and select the hydraulic press brake that best suits your needs and requirements.






Reviewed by 1 user
press brake
Excellent Press brake machine supplier, we bought from your company in 2015 and have been using, very good.