When choosing a fiber laser metal cutting machine, material compatibility is a crucial factor. Different metals and alloys have varying properties that affect how they respond to laser cutting. The machine's specifications, such as power, speed, and lens type, must align with the materials you plan to process to achieve optimal results. Understanding which materials the machine can handle effectively ensures you make an informed decision and invest in equipment that meets your production needs and delivers high-quality cuts.
Overview of Fiber Laser Cutting Technology
Fiber laser cutting technology utilizes a highly concentrated beam of light to precisely cut through metal materials. This technology operates by focusing a laser beam onto the material, which heats it to the point of melting or vaporization, resulting in clean and accurate cuts. Fiber lasers are known for their exceptional precision, speed, and efficiency compared to traditional cutting methods. They offer significant advantages including reduced energy consumption, lower operating costs, and the ability to cut a wide range of materials with minimal maintenance.
Understanding Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines
How fiber lasers work for metal cutting
Metal laser cutting involves a highly concentrated laser beam that’s directed onto the metal surface. The heat from the laser melts or vaporizes the metal, producing a clean, accurate cut. Here are the main stages of metal laser cutting:
Designing the cutting pattern: Before the actual cutting, the design or pattern is created in CAD or other graphic software.
Configuring the laser cutter: The operator sets the power, speed, and focus of the laser according to the type and thickness of the metal.
Cutting the metal: The laser cutter follows the design pattern, cutting through the metal with high precision.
Cooling and post-processing: After cutting, the metal parts are cooled and any residual debris is removed. Additional post-processing steps may include deburring or applying protective coatings.
Key features
Precision: Fiber lasers offer exceptional precision due to their focused beam and high-quality optics. This enables detailed and intricate cuts with tight tolerances, making them ideal for complex metal parts and components.
Speed: Fiber lasers are known for their high cutting speeds. They can process materials faster than traditional methods, increasing overall productivity and reducing production times.
Efficiency: Fiber lasers are highly efficient in converting electrical energy into laser light, leading to lower operating costs. They require less maintenance and have a longer service life compared to other laser technologies, contributing to lower long-term expenses.

What Are Two Types of Lasers for Metal Cutting
There are two primary types of laser cutters used for metal cutting: fiber laser cutters and CO2 laser cutters. Each type has its own distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Fiber Laser Cutters
Fiber laser cutters are renowned for generating narrower beams, which effectively provide about four times the power for the same laser output energy compared to CO2 lasers. These machines operate with greater speed and precision, making them ideal for high-precision cuts on thinner metal parts. Additionally, fiber lasers have lower operating costs due to their electrical efficiency and solid-state construction. However, they require more nitrogen shielding gas during the cutting process.
CO2 Laser Cutters
CO2 laser cutters, on the other hand, produce a wider cutter beam width and are capable of higher device power. They excel in lower-precision cuts on thicker metal parts. While the initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) for CO2 laser cutters is lower than that of fiber lasers, their operating expenses (OPEX) are higher per length of cut. This makes CO2 lasers suitable for applications where precision is less critical and thicker materials need to be processed.
Types of Metals for Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine
Steel
Carbon Steel: Fiber laser metal cutting machines can efficiently cut carbon steel with clean edges. The cutting characteristics depend on the carbon content and thickness. For thin sheets, fiber lasers provide fast and precise cuts, while thicker carbon steel may require adjustments in power and speed settings to achieve optimal results.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel's properties, such as corrosion resistance and strength, make it suitable for a variety of applications. Fiber lasers can handle stainless steel well, with settings adjusted to prevent oxidation and achieve smooth edges. Optimal settings often involve high power and speed to maintain the material's integrity.
Alloy Steel: Cutting alloy steel with fiber lasers involves understanding the specific alloy composition. Each alloy may require different cutting parameters to ensure quality cuts without compromising the material's properties.
Aluminum
Types and Thicknesses: Fiber lasers can cut various types of aluminum, including pure aluminum and aluminum alloys. The machine's power and speed settings must be adjusted according to the thickness. For example, thicker aluminum may require higher power and slower speed to ensure a clean cut
Special Considerations: Aluminum's reflective nature poses challenges for fiber laser cutting. It requires careful management of laser settings and sometimes the use of special coatings or gases to enhance the cutting process.
Copper and Brass
Challenges and Techniques: Copper and brass are highly reflective and conductive, making them challenging to cut with fiber lasers. Techniques such as using a high-frequency pulsed laser and optimizing gas flow can help achieve precise cuts. It's crucial to manage heat dissipation to prevent material damage.
Factors Influencing Material Suitability
Laser Power and Wattage
The power of the laser directly influences its ability to cut through different materials. Higher wattage lasers can cut through thicker and denser materials with greater ease. For instance, a 1,000W laser might be sufficient for cutting thin sheets of stainless steel or aluminum, but thicker materials or tougher metals like titanium or alloy steel would require higher power levels to ensure clean cuts without excessive heat buildup or material warping.
Material Thickness
Different metals have specific optimal thickness ranges for fiber laser cutting. For carbon steel, fiber lasers can cut up to 20mm thick, whereas for stainless steel, the limit is generally around 15mm. Aluminum typically has an optimal cutting range up to 10mm, and copper or brass can be efficiently cut up to 5mm. Exceeding these ranges can compromise the quality of the cut and the efficiency of the process.
Cutting Speed and Quality
The speed at which the laser cuts the material impacts both the quality of the cut and the efficiency of the operation. Faster cutting speeds can increase productivity but may reduce the precision and smoothness of the cut edges, especially on thicker materials. Conversely, slower cutting speeds can improve cut quality and precision but may lead to higher production times. Finding a balance is crucial for achieving the desired quality while maintaining operational efficiency..
Machine Settings and Parameters
Each material requires specific settings to achieve optimal cutting results. Parameters such as laser power, cutting speed, focus position, and gas pressure need to be adjusted according to the material being processed. For instance, cutting aluminum might require higher gas pressure to prevent oxidation, while cutting stainless steel might need precise focus adjustments to avoid edge burning. Properly calibrating these settings ensures high precision and quality cuts across various materials.

Explore Metal Laser Cutting Process
What are the main parts of a metal laser cutter?
Fiber laser metal cutting machine is composed of several key components:
- Laser resonator: This is where the laser beam is generated.
- Cutting head: This component houses the focusing lens that directs the laser beam onto the metal surface.
- CNC controller: The computer numerical control (CNC) system controls the machine’s movements and operations based on the design inputs.
- Gas delivery system: This system delivers assist gas to the cutting head to help eject molten metal and minimize oxidation.
- Chiller: This part cools the machine components to prevent overheating during operation.
What are the main parameters of metal laser cutting process?
When cutting metal with a laser, several parameters must be carefully managed to achieve the desired results:
- Laser power: This refers to the amount of energy that the laser can deliver, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
- Cutting speed: This is the speed at which the laser cutter moves across the material. It directly affects the cut quality and efficiency.
- Pulse frequency: This is the number of laser pulses per second. It can affect the cut quality, speed, and the overall heat affected zone (HAZ).
- Focus spot size: This is the diameter of the laser beam at its focal point. Smaller spot sizes result in narrower cuts and higher cut quality.
- Assist gas pressure: The assist gas helps eject molten material and minimize oxidation. Its pressure must be correctly set depending on the type and thickness of the material.
What are the cutting tolerances for metal laser cutting?
The typical laser cutting tolerances for metals are:
- For thin sheet metal (up to 1mm): +/- 0.1mm to +/- 0.2mm
- For medium thickness sheet metal (1mm to 5mm): +/- 0.2mm to +/- 0.5mm
- For thicker materials (over 5mm): +/- 0.5mm to +/- 1.0mm
What is the max thickness can laser cut?
The thickness of metal that can be cut with a laser depends on the type of laser and its power. Generally, a laser can cut steel up to 1 inch (25.4mm) thick, stainless steel up to 0.75 inches (19.05mm), and aluminum up to 0.5 inches (12.7mm).
What is the best metal for laser cutting?
The best metal for laser cutting depends on the specific application and requirements. However, mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are among the most commonly used due to their excellent machinability and compatibility with laser cutting.
Physical and chemical properties for materials
Mild Steel (Carbon Steel)
Mild steel, also known as carbon steel, is a popular choice for laser cutting. It’s affordable, durable, and offers excellent weldability. With carbon content up to 0.3%, it’s not as brittle as higher-carbon steels.
- Melting point: 2,600 to 2,800 degrees Fahrenheit
- Tensile strength: 370-500 MPa
- Specific gravity: 7.85
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy that’s ideal for a wide range of laser cutting stainless steel applications. It offers good strength and excellent resistance to oxidation.
- Melting point: 2,550 to 2,750 degrees Fahrenheit
- Tensile strength: 515 MPa
- Specific gravity: 7.93
Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight, soft, and ductile metal with excellent corrosion resistance thus making aluminum laser cutting ideal for a range of industrial applications.
- Melting point: 1,220 degrees Fahrenheit
- Tensile strength: 90-140 MPa
- Specific gravity: 2.70
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. It’s easy to machine, has good corrosion resistance, and is excellent for decorative purposes.
- Melting point: 1,650 to 1,720 degrees Fahrenheit
- Tensile strength: 345-470 MPa
- Specific gravity: 8.4-8.73
Copper
Copper has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is tough, ductile, and can be readily welded and soldered.
- Melting point: 1,984 degrees Fahrenheit
- Tensile strength: 210-360 MPa
- Specific gravity: 8.96
Advantages of Fiber Laser for Metal Cutting
Precision
Fiber laser cutting machines offer unparalleled precision, enabling intricate and complex cuts with minimal material waste. The high-powered laser beams can cut through various metals with exceptional accuracy, ensuring high-quality finished products. This level of precision is critical for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where exact specifications and tolerances are mandatory. The smooth and clean edges produced by these machines eliminate the need for secondary operations, enhancing the efficiency of metal fabrication processes.
Speed
Fiber laser cutters operate significantly faster than conventional cutting machines, resulting in faster production turnaround times. This increased speed boosts productivity and reduces lead times, allowing for more efficient manufacturing processes. The rapid cutting capabilities of fiber laser machines enable manufacturers to meet tight production schedules and respond quickly to customer demands. This agility is particularly valuable in industries requiring quick turnaround times, such as automotive manufacturing and just-in-time production processes.
Versatility
Laser cutting machines can process a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, making them ideal for various metal fabrication applications. Their ability to create intricate designs and shapes ensures they meet diverse customer requirements. The precision and accuracy of laser cutters minimize material waste and reduce the need for secondary operations, resulting in faster production times and lower costs. The versatility of laser cutting machines makes them indispensable tools for a wide range of industries.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in fiber laser cutting machines may be higher, the long-term cost savings are substantial. Their efficiency and accuracy reduce material waste and minimize the need for secondary operations, ultimately lowering production costs. The speed and precision of these machines result in significant time savings, increasing productivity and output. Additionally, the versatility of laser cutting machines allows a single machine to handle various materials and applications, saving on equipment costs and optimizing floor space.
Minimal Maintenance
Fiber laser cutting machines are known for their reliability and low maintenance requirements. With fewer moving parts and a solid-state laser source, these machines have a longer lifespan and require less frequent maintenance, resulting in increased uptime and productivity. This minimal maintenance reduces overall operating costs and ensures consistent performance over time. The solid-state laser source in fiber laser cutters simplifies operation and reduces the need for frequent part replacements, making them a reliable and cost-effective solution for metal fabrication.
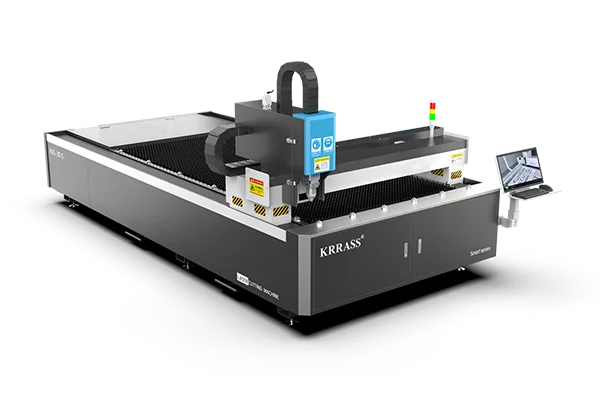

Fiber Laser vs. CO2 Laser: Which is Better for Metals
1. Laser generator
The carbon dioxide laser is a gas molecule laser, with CO2 as the medium and O2, He, Xe, etc. as the auxiliary gas. The beam is transmitted and focused to the laser cutting head through the reflector. While the fiber laser cutting machine transmits the laser beam through diodes and optical fiber cables. Multiple diodes pump the laser beam and then transmit it to the laser cutting head through flexible optical fiber cables. In CO2 laser technology, the reflector should be used at a certain distance, but the fiber one will not be subject to such restrictions.
2. Conversion rate
Fiber laser is an advanced laser technology at present. The solid-state laser generator it uses is more efficient than the traditional carbon dioxide laser. The photoelectric conversion rate of the carbon dioxide laser cutter is only 8% - 10%, while it of the fiber laser cutter can be as high as 30%. That is to say, the overall energy consumption of the fiber laser cutter is 3-5 times lower than the overall energy consumption of the CO2 one, thus improving the energy efficiency by at least 86%, saving more power and also saving more production costs.
3. Cutting ability
The fiber laser has shorter wavelength which is only 1/10 of the wavelength generated by the CO2 laser, which can improve the absorption of the cutting material to the beam, and is more suitable for conducting in the thin and soft fiber. Compared with carbon dioxide laser transmitted by mirror reflection, fiber laser should be flexible and easier to maintain. A 3KW fiber laser cutting machine is equivalent to a 4-5KW CO2 laser cutting machine in cutting capacity and speed, greatly reducing operating costs.
4. Maintenance cost
The structure of CO2 laser is relatively complex, and the maintenance cost in the later stage is relatively high. Moreover, the CO2 laser system should be cleaned and maintained regularly, and the reflector should also be cleaned and calibrated regularly. In addition, due to the purity of carbon dioxide gas, the resonator should also be maintained regularly. Besides, the turbine transporting laser gas also needs regular maintenance and overhaul. The fiber laser cutting is basically maintenance free, with few vulnerable parts. It can withstand harsh working environment and has high resistance to dust, impact, humidity and temperature, thus its maintenance cost is low.
5. Processing material
The beam wavelength of CO2 laser is 10.64um, which is easier to be absorbed by non-metallic materials. However, the wavelength of the fiber laser is only 1.064um, which is 10 times shorter than the CO2 laser's. Due to this smaller focal length, the intensity of the fiber laser cutter is almost 100 times higher than that of the CO2 laser cutter with the same power output. Therefore, fiber laser cutting machine is very suitable for cutting metal materials.
The CO2 laser cutting machine is mainly used for cutting and carving non-metallic materials, such as wood, acrylic, paper, leather, fabric, etc., because of its low efficiency in cutting and carving metal materials. Fiber laser cutting machine, also known as metal laser cutting machine, is mainly used for metal materials. Such as stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized steel, copper, aluminum, etc.
Final Thought
Carefully evaluate your material needs and the specific features of fiber laser metak cutting machines to ensure the best investment decision. KRRASS offers a range of advanced fiber laser cutting machines and expert guidance to help you select the ideal solution for your metal fabrication requirements.





Reviewed by 1 user
I have been paying attention to KRASS. This professional knowledge is very helpful.