I.Introduction
The laser cutting head is a core component of a laser cutting machine, directly impacting cutting accuracy, speed, and quality. It focuses the laser beam into a high-energy spot, which then cuts the material surface. Its performance directly impacts cutting accuracy, speed, and quality. The following details its operating principle, structure, core parameters, classification, and key purchasing considerations.
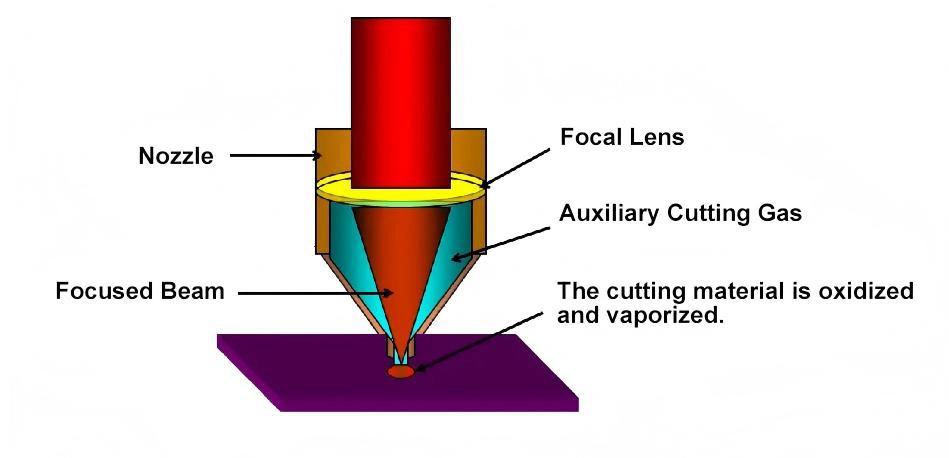
The laser cutting head operates by focusing a high-energy laser onto the material surface through a focusing system. Upon absorption of the laser energy, the material’s local temperature rapidly rises above its melting point. Simultaneously, a nozzle coaxial with the beam ejects high-pressure gas, dislodging the molten metal and creating a cavity on the material’s surface. As the laser cutting head moves according to a programmed process, it ultimately cuts the material into the desired shape. Based on the cutting principle, it can be categorized into four types: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting cutting, laser oxygen cutting, and laser scribing and controlled fracture.
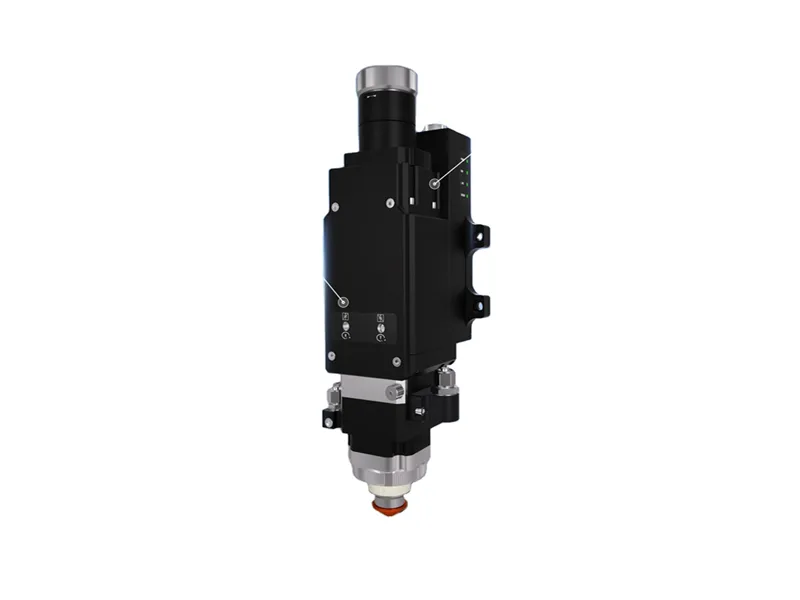

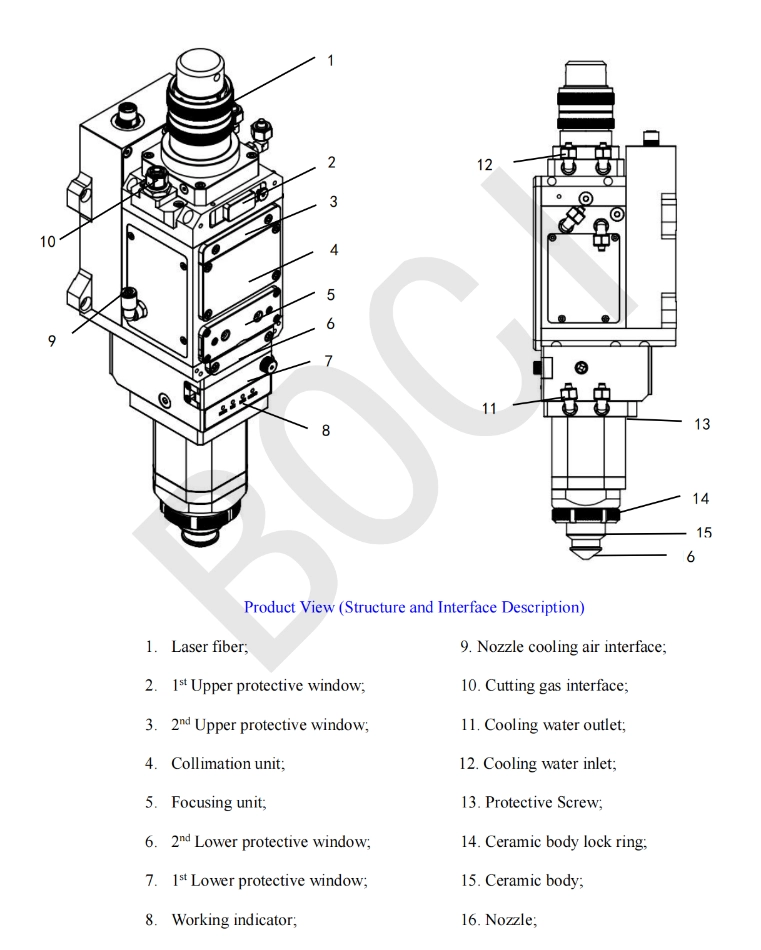
II.The basic structure of laser cutting head
Collimator: Converts the divergent laser beam output by the laser into parallel light, ensuring uniform energy distribution during transmission and providing a stable light source for subsequent focusing. Materials commonly used are quartz or zinc selenide (adapted to the laser wavelength; for example, zinc selenide is commonly used for CO₂ lasers).
Focusing lens: Focuses the parallel light into an extremely small spot (down to micrometers in diameter), highly concentrating the energy and achieving instant melting or vaporization of the material. The focal length determines the spot size and working distance (the shorter the focal length, the smaller the spot and the closer the working distance). The selection should be based on the thickness of the cutting material and the required precision.
Nozzle: Injects auxiliary gas (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air) to remove slag generated during cutting, preventing it from adhering to the material surface or damaging the focusing lens. It also assists combustion (for example, oxygen is used when cutting carbon steel) or inhibits oxidation (for example, nitrogen is used when cutting stainless steel). Nozzles are categorized by shape into round and square; and by aperture into sizes of 0.8mm, 1.0mm, and 1.5mm, depending on the material type and thickness (e.g., large-aperture nozzles are used for thick plate cutting).
Tracking Sensors: The sensing and feedback system is crucial for achieving automated and intelligent laser cutting. This system primarily includes various sensors, such as height sensors, temperature sensors, and laser power sensors. The height sensor monitors the distance between the cutting head and the plate surface in real time and feeds this data back to the control system, ensuring the cutting head maintains the optimal cutting height and preventing degradation of cutting quality due to uneven plate surfaces or plate deformation during cutting.
The temperature sensor monitors temperature changes during the cutting process, providing a basis for adjusting laser power and cutting speed to prevent excessively high or low temperatures from affecting cutting results. The laser power sensor monitors laser output power in real time, ensuring laser power stability and ensuring consistent and reliable cutting. The sensing and feedback system works in conjunction with the control system to enable real-time monitoring and automatic adjustments of the cutting process, improving cutting quality and production efficiency. Protective lens: Located in front of the focusing lens, it blocks slag and dust flying during the cutting process, protecting the expensive focusing lens from contamination or damage. This is a consumable part and requires regular replacement.
Cooling system: Available in two types: water-cooling and air-cooling. Water-cooling systems remove heat through circulating coolant and are suitable for high-power cutting operations. Air-cooling systems use air flow to reduce temperatures and are suitable for medium- and low-power cutting tasks. This prevents overheating of the cutting head, extends its service life, and ensures a stable cutting process.
Control module: Responsible for managing laser beam emission, focal length adjustment, auxiliary gas flow control, and other parameter adjustments. By interoperating with a CNC or automation system, it enables precise cutting operations and automated production.
Fiber optic transmission system: Primarily used in fiber laser cutting heads, it transmits the laser beam generated by the laser to the cutting head. It features high efficiency and stability, ensuring that the laser beam maintains energy during long-distance transmission.
Gas control system: The gas control system plays a crucial role in the laser cutting process. During the cutting process, high-pressure gas is injected into the cutting area. Its primary functions include blowing away slag generated by cutting to ensure a clean cut seam; protecting the focusing lens from slag splashing and damaging it; and assisting the laser in cutting the sheet metal, improving cutting speed and quality. The gas control system primarily consists of a gas nozzle, gas piping, a gas flow control valve, and a gas pressure regulator. The design and position of the gas nozzle significantly influence the gas injection effect. Different cutting processes and sheet metal materials require different gas nozzle types and structures. The gas flow control valve and pressure regulator are used to precisely control the gas flow and pressure to suit different cutting requirements.
III.Core parameters of laser cutting head (key factors affecting cutting performance)
Focused spot diameter directly determines energy density: Smaller spot sizes (e.g., 20-50μm) result in higher energy density, making them suitable for fine cutting (e.g., thin metal sheets and precision parts); larger spot sizes are more suitable for thick plate cutting (requiring higher power).
Related to focal length and beam quality: A short focal length focusing lens (e.g., 50mm) produces a smaller spot size, while a long focal length (e.g., 150mm) is suitable for thick plate cutting or cutting steep slopes.
Working distance: This refers to the distance from the nozzle tip to the material surface and must match the focal length of the focusing lens. Too close a working distance can easily cause the nozzle to collide with the material, while too far a distance reduces energy density, affecting cutting quality.
Adjustment range: This includes the focal length adjustment range (to accommodate varying material thicknesses) and the tracking height adjustment range (to accommodate surface undulations). The wider the range, the more versatile the device. Compatible Laser Type and Power: The laser must match the wavelength (e.g., 1064nm fiber laser, 10.6μm CO₂ laser) and power. High-power lasers (e.g., 6000W and above) require a cutting head with enhanced heat dissipation and damage resistance (e.g., water cooling and high-threshold lenses).
Response Speed: The response speed of the sensor detection and adjustment device affects stability during high-speed cutting (e.g., when cutting curves or sharp corners, the tracking height must be adjusted quickly to avoid edge burning or wire breakage).
IV.Common classification of laser cutting heads (according to the type of laser adapter)
Fiber laser cutting head: Compatible with 1064nm fiber lasers, widely used for cutting metal materials (carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc.). Features include compact structure, high power tolerance, and high focusing accuracy, making them suitable for medium- to high-power cutting applications (1000W-30,000W).
CO₂ laser cutting heads: Compatible with 10.6μm CO₂ lasers, primarily used for cutting non-metallic materials (wood, acrylic, fabric, etc.) and some thin metals. They require lenses made of infrared-transmissive materials (such as zinc selenide), are more sensitive to ambient dust, and require enhanced protection.
UV laser cutting head: Compatible with UV lasers (such as 355nm), used for high-precision micro-cutting (e.g., PCBs, sapphire, and thin film materials). Features include an extremely small spot size (down to less than 10μm) and a minimal heat-affected zone, making them suitable for the precision electronics industry. Solid-state lasers (such as Nd:YAG, 1064nm wavelength; Nd:YVO₄, 1064nm wavelength) have similar optical designs to fiber laser cutting heads (same wavelength), but require adaptation to the solid-state laser’s pulse mode. Many have integrated pulse energy modulation modules, making them suitable for pulsed cutting (reducing thermal deformation). Advantages: Extremely high cutting accuracy (μm level) in pulsed mode. Disadvantages: Low power limit (mostly < 500W) and low efficiency, leading to their gradual replacement by high-power fiber lasers.
V. Key Points for Selecting Laser Cutting Heads
- Match the laser parameters: Ensure that the wavelength compatibility and power tolerance of the cutting head are consistent with the laser (for example, a high-power fiber laser requires a dedicated high-power cutting head).
- Consider the material and thickness to be cut: For thin materials and fine cutting, choose a short focal length and small spot size cutting head; for thick materials, select a long focal length and large aperture nozzle, and ensure that the adjustment range covers the material thickness.
- Pay attention to stability and durability: Prioritize products with efficient heat dissipation (water cooling), high wear-resistant nozzles, and easy-to-replace protective lenses to reduce maintenance costs.
- Automation functions: For batch production or complex workpieces, choose cutting heads with automatic focusing and high-response speed tracking systems to improve efficiency and consistency.
- Brand and after-sales service: Cutting heads from well-known brands (such as Precitec, Raytools, and Wanshunxing) have more stable performance and a complete after-sales service network, making them suitable for long-term use.
VI. Application Scenarios
- Metal processing: Planar cutting of stainless steel plates, iron plates, aluminum alloys, etc. (using fiber laser cutting heads).
- Non-metal processing: Acrylic engraving and cutting, fabric cutting, wood carving (using CO₂ laser cutting heads).
- Precision manufacturing: Micro-cutting of mobile phone screens, electronic components, medical devices (using ultraviolet or high-precision fiber cutting heads).
VII. Laser Cutting Head Brands
Domestic brands of laser cutting heads focus on cost-effectiveness and local services, constantly innovating and breaking through in technology; while foreign brands, relying on their profound technical accumulation and advanced manufacturing processes, have gained certain advantages in the high-end market. Here are some common introductions of domestic and foreign brands:
Precitec Laser Cutting Head: One of the leaders in the global laser cutting head field, renowned for its outstanding auto-focusing function and high efficiency. Its cutting head can automatically adjust the focal length according to the material thickness and type, is made of high-quality materials, can withstand extremely high cutting power, and is suitable for various types of laser cutting equipment such as fiber lasers and CO₂ lasers, widely used in the high-precision metal cutting field.
IPG Photonics Laser Cutting Head: A globally renowned manufacturer of fiber lasers, its laser cutting head is known for its efficient beam transmission and stability. The cutting head of IPG works well with fiber lasers and can handle high-power lasers, suitable for the cutting of large thickness metals. It performs well in the automotive manufacturing, aerospace and other industries, and has low maintenance costs.
Trumpf Laser Cutting Head: A well-known German company in the field of laser processing equipment, its laser cutting head has extremely high precision, suitable for thin metals and complex shapes. Equipped with intelligent sensors and an automatic focusing system, it can automatically adjust the cutting parameters. The product design focuses on service life, has good corrosion resistance and durability, and is suitable for long-term mass production.
BOCHI Laser Cutting Head: The BOCHI cutting head is a product of Shanghai Bochi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., which has a high reputation in the field of laser cutting control. It has multiple product series for different power ranges and application scenarios. For example, BLT310 is a highly cost-effective intelligent cutting head developed for medium and low power; BLT6 is an intelligent cutting head developed for ultra-high power laser equipment, with a maximum power support of 40kW; and there are also multi-product combinations such as 3T, 4T, 5H series for pipe cutting applications. For example, BLT310 is small in size, lightweight, and integrates multiple sets of intelligent sensors, which can perform real-time closed-loop intelligent monitoring, quickly diagnose and warn in time. It is equipped with a standard air pressure sensor, has more precise gas control, more stable cutting surface quality, and has an opening protection function to avoid lens explosion. In addition, its focusing speed is faster, the focusing range is wider, the perforation is more efficient, and it supports more cutting processes.
Raytools Laser Cutting Head: A domestic laser cutting head manufacturer in China, it has won a wide market with high cost-effectiveness and strong technical support. Its cutting head is suitable for various laser systems such as fiber lasers and CO₂ lasers, and its product line covers the requirements from low power to high power. The design simplifies the operation and maintenance process, reducing downtime.
WSX Laser Cutting Head: Focusing on the research and development of efficient and stable laser cutting heads, it performs well in precision metal processing and thin sheet cutting. The product has automatic focusing and intelligent sensors, which can automatically optimize cutting parameters according to material changes, and also provides comprehensive technical support and after-sales service.
Han’s Laser: A brand under Daqin Laser, its products such as RC304 three-dimensional five-axis cutting head have advantages in three-dimensional irregular surface cutting, breaking the control of a few industry giants abroad, representing the current highest technical level of CNC machine tools in the world.
Summary:
The selection of laser cutting heads should follow the principles of “parameter coordination, performance adaptation, and scenario focus”. Through scientific testing and data accumulation, a precise process system can be established. For example, a certain automotive component enterprise improved the cutting efficiency of stainless steel by 35% and reduced the defect rate from 5% to 1.2% by introducing BOCU’s “BL310” cutting head and process database, verifying the value of systematic selection. In the future, with the deep integration of AI and IoT technologies, cutting heads will develop towards “self-sensing, self-decision-making, and self-optimization”, further promoting the intelligent upgrade of laser processing. If you need more information about laser cutting heads, please contact us!