Both Vertical V Grooving Machine and Horizontal V Grooving Machine are equipment used for slotting on the surface of materials. However, they have significant differences in structural design, applicable scenarios, and performance characteristics. So, how do we choose between them? Below, we will take a detailed look at the differences between the two from multiple dimensions to help you make a better choice when selecting a slotting machine.

Horizontal V Grooving Machine

Vertical V Grooving Machine
Table of Contents
Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:working principles
1.1Vertical V Grooving Machine
The Vertical V Grooving Machine is based on the core concept of “vertical spindle cutting + horizontal feed”. The overall process can be divided into three steps: power output, cutting execution, and feed control.

(1) Power transmission and tool drive
Spindle layout:The spindle is perpendicular to the work platform (in the Z-axis direction), driven directly by a motor (usually a variable frequency motor or servo motor) through belts, gears or couplings, and drives the slotting tools (such as milling cutters, slotting cutters, saw blades, etc.) installed at the end of the spindle to rotate at high speed (the rotational speed is usually 1000-5000 r/min).
(2)Cutting Execution Process
Tool Contact: Fix the workpiece on a horizontal worktable (using fixtures, vacuum suction, or manual pressing), manually or electrically adjust the height of the spindle (Z-axis feed) to make the rotating tool contact the surface of the workpiece. Utilize the shear force of the tool edge to remove the material and form initial groove marks.
Groove Shape Control: By limiting the tool diameter (to control the width of the groove) and the depth of the spindle descent (to control the depth of the groove), combined with the tool type (such as V-shaped cutter for inclined grooves, straight cutter for rectangular grooves), a specific shape of the groove body is formed.
(3)Feed motion control
Horizontal feed: The workpiece or the tool moves in a straight line along the X/Y axes (horizontal direction) – for smaller models, the workpiece is usually manually pushed (such as the arm-type Vertical V Grooving Machine), while for slightly larger models, the worktable or the tool slide is driven by a servo motor to achieve uniform feed (feed speed 0.5 – 5m/min), ensuring the straightness of the groove body.
Compound motion: Some CNC Vertical V Grooving Machines can achieve coordinated movement of the X/Y/Z axes through program control, enabling the processing of complex groove types such as curved grooves and intermittent grooves (such as the arc-shaped grooves of advertising characters).
1.2.Horizontal V Grooving Machine
The Horizontal V Grooving Machine relies on “rigid support of the gantry frame + multi-axis coordinated cutting”, with the core being high-power cutting + wide range of feed. It is suitable for heavy-duty processing, and the working process is divided into three stages: rigid fixation, heavy-load cutting, and coordinated feed:

(1) Rigid Fixation and Power Configuration
Workpiece Fixation: Large-sized workpieces (such as thick steel plates) are firmly fixed on the heavy-duty worktable (the table surface has undergone aging treatment, with minimal deformation) using T-slot bolts, hydraulic fixtures, or electromagnetic suction cups, ensuring no displacement or vibration during processing.
Power System: The main spindle box on the crossbeam is equipped with a high-power motor (11-55kW) and a reduction mechanism, driving the cutting tool to rotate at low speed with high torque (usually at 300-2000r/min). Some models adopt a dual-spindle design, allowing for multi-slot processing simultaneously. The cutting tools are mostly made of hard alloy or diamond, suitable for cutting high-hardness materials.
(2) Heavy-load Cutting Logic
Cutting Force Balance: The rigid structure of the gantry frame (columns + crossbeam) can counteract the radial and axial forces generated during cutting (especially when processing thick steel plates, the cutting force can reach several tons), avoiding tool vibration or workpiece deformation, and ensuring the verticality and surface finish (Ra ≤ 1.6μm) of the groove wall.
Deep Slot Processing Strategy: For slots deeper than 50mm, the “layered cutting” method is adopted – each time cutting 2-5mm deep, the spindle descends multiple times to stack, combined with the cooling system (emulsified liquid or cutting oil) for cooling and chip removal, preventing tool overheating and wear.
(3) Multi-axis Coordinated Feed
Axis Movement:
X-axis: The cutting tool moves horizontally along the crossbeam (traveling range can reach 5-10m), controlling the length direction of the groove body;
Y-axis: The worktable moves along the guide rail longitudinally (traveling range 3-8m), controlling the width direction of the groove body;
Z-axis: The main spindle box moves up and down along the columns, controlling the depth of the slot opening;
Some models are equipped with a C-axis (tool rotation axis), enabling inclined slot and helical slot processing.
Numerical Control Coordination: Through CNC numerical control system programming (such as Siemens, Fanuc systems), the X/Y/Z axes are synchronized to achieve continuous slotting (such as long straight slots on steel plates), array slots (uniformly distributed multiple slots), or irregular slots (such as the zigzag slots on ship steel plates), with feed speed up to 1-10m/min, and motion accuracy controlled within 0.01mm/300mm.
1.3.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Summary of Core Principles Comparison
| Stage | Vertical V Grooving Machine | Horizontal V Grooving Machine |
| Power core | Low-power vertical spindle, focusing on medium-speed and light-load cutting. | High-power spindle box, focusing on low-speed heavy-load cutting, relies on the rigidity of the frame to resist vibration. |
| Feed logic | Mainly uses manual or single-axis electric feed, suitable for simple straight/curved grooves. | Multi-axis CNC linkage, supporting continuous processing of complex trajectories, with a wide feed range. |
| Cutting strategy | One-time cutting and forming, suitable for shallow grooves and narrow grooves. | Layered cutting, suitable for deep slots, wide slots and high-strength materials. |
| Precision guarantee | Dependent on the flatness of the worktable and the stability of the spindle, with medium precision. | Relying on the rigidity of the gantry frame and the CNC system, the accuracy is higher (especially for large workpiece processing). |
2.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Structural design differences
2.1. Vertical V Grooving Machine
Core structure: Adopting a “vertical” layout, the main shaft (tool installation shaft) is arranged in a vertical direction. The work platform is mostly horizontally fixed or moves within a small range. The tool mainly achieves slot depth control through the vertical direction (Z-axis) of elevation. Some models are equipped with a fine adjustment mechanism in the horizontal direction (X/Y-axis).
Frame features:The overall height of the body is relatively high, and the structure is relatively compact. There are no large crossbeams or column supports. The center of gravity is more inclined towards the vertical direction.
2.2. Horizontal V Grooving Machine
Core structure: Adopting a “vertical” layout, the main shaft (tool installation axis) is arranged in a vertical direction, and the work platform is mostly horizontally fixed or moves within a small range. The tool mainly achieves slot depth control through the vertical direction (Z-axis) of the lifting. Some models are equipped with a fine adjustment mechanism in the horizontal direction (X/Y-axis).
Frame core structure: Adopting a “gantry” frame, consisting of two vertical columns and a crossbeam spanning the columns, forming a “gate” structure. The crossbeam can move up and down along the columns (Z-axis), the tool is installed on the crossbeam and can move horizontally along the crossbeam (X-axis), and the work platform is mostly a large horizontal platform (which can move along the Y-axis).
Frame features: Extremely rigid, the crossbeam and the columns form a stable rectangular frame, capable of withstanding heavy-load processing, and the overall area is large.
3.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Applicable to differences in workpieces
3.1.Vertical V Grooving Machine
Workpiece size: Suitable for medium-sized and lightweight workpieces, such as plates (metal plates, acrylic plates, wood plates) with a thickness of ≤ 50mm, small profiles (square tubes, angle irons), etc. The length/width of the workpiece is usually no more than 2 meters.
Workpiece weight: Due to the limited load-bearing capacity of the work platform (generally ≤ 500kg), it is not suitable for extremely heavy workpieces.
3.2.Horizontal V Grooving Machine
Workpiece size: Specifically designed for large and heavy workpieces, capable of processing sheet materials with a length of over 5 meters and a width of over 3 meters (such as thick steel plates, stone materials, composite material plates), and even able to handle large-sized rolls (requires a feeding mechanism).
Workpiece weight: The work platform can bear a weight of several tons (some heavy-duty models ≥ 10 tons), suitable for processing thick steel plates (thickness ≥ 100mm) in shipbuilding, bridges, and heavy machinery.
4.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Processing performance differences
| Dimension Processing | Vertical V Grooving Machine | Horizontal V Grooving Machine |
| Slotting accuracy | suitable for general precision requirements (such as slotting for advertising characters, positioning slots for small parts). | High precision (within ±0.05mm), the rigidity of the gantry frame can reduce processing vibrations, and is suitable for deep and narrow groove processing of precision fixtures and molds. |
| Slotting depth / width | The depth is usually ≤ 30mm, the width is ≤ 20mm, limited by the spindle power and structural stability. | The depth can reach over 100mm, and the width can be adjusted to over 50mm according to the tool. It supports continuous processing of deep and wide grooves. |
| efficiency | The single-slot processing efficiency is medium, suitable for small batch, multi-variety processing, with short tool change / adjustment time. | The batch processing efficiency is high. Through the linkage of the crossbeam and the platform, multi-slot continuous processing can be achieved, suitable for large-scale standardized slotting (such as steel plate splicing slots). |
| Material adaptability | Suitable for non-metallic materials (wood, acrylic), thin metals (aluminum, copper, thin steel), etc., with low hardness / low strength. | It can process high-strength metals (thick steel plates, alloy steels), stone, glass fiber boards and other hard and brittle / high-hardness materials. |
5.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Application scenario differences
5.1. Vertical V Grooving Machine
Industry field: Advertising production (acrylic letter slotting), furniture manufacturing (wood board joint slotting), small hardware processing (electrical component positioning slotting), decoration and renovation (aluminum profile slotting), etc.
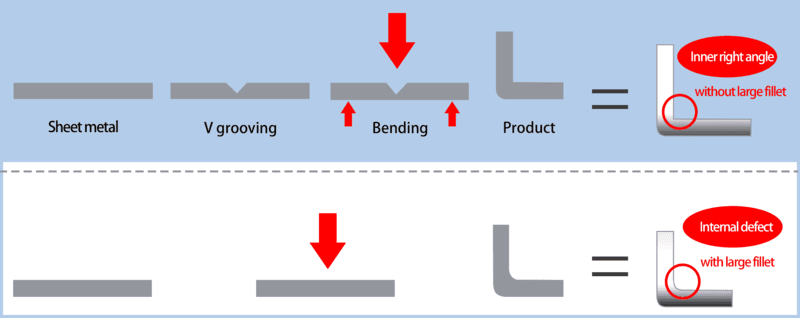
Typical case: Slotting a 5mm wide and 2mm deep groove on a 3mm thick aluminum plate for later bending and forming.
5.2. Horizontal V Grooving Machine
Industry field: Advertising production (acrylic letter slotting), furniture manufacturing (wood board joint slotting), small hardware processing (electrical component positioning slotting), decoration and renovation (aluminum profile slotting), etc.
Typical case: Slotting on a 3mm thick aluminum plate
6.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Other key differences
| Dimension | Vertical V Grooving Machine | Horizontal V Grooving Machine |
| Floor area | Small (usually no more than 2 square meters), suitable for corners of workshops or small factories. | Large (usually ≥ 10 square meters), requiring a dedicated workshop area. Some models need to be fixed on a foundation. |
| Equipment cost | Low (ranging from several thousand yuan to tens of thousands of yuan), suitable for initial investment by small and medium-sized enterprises. | High (ranging from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of yuan), suitable for large-scale production or heavy processing enterprises. |
| Operational complexity | Simple, beginners can operate it after a short training period. | Complex, requiring professional operation. Some models need to be programmed in conjunction with a CNC system. |
7.Vertical V Grooving Machine VS Horizontal V Grooving Machine:Operating Costs
Energy Consumption: The Horizontal V Grooving Machine has a large power capacity (with a daily electricity consumption of 50-200 kWh), which is 3-5 times that of the vertical machine.
Tool Wear: For processing hard materials, high-frequency replacement of carbide tools is required (the cost is 5-10 times that of high-speed steel tools).
Maintenance: The maintenance cost of the CNC system is higher than that of manual models. A yearly maintenance budget needs to be reserved (approximately 1-3% of the total equipment price).
The Vertical V Grooving Machine has the core advantages of “flexibility, compactness and low cost”, making it suitable for small-scale processing of medium-sized and thin workpieces. The Horizontal V Grooving Machine, on the other hand, is characterized by “strong rigidity, high precision and large load capacity”, and is specifically designed for efficient and precise processing of large and heavy workpieces. When making a choice, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the size of the workpiece, material type, production scale and precision requirements. Now, do you know how to make the choice?